Table of Contents
Stainless steel is a highly versatile material used across a wide range of industries, from household kitchenware to complex aerospace parts. What gives stainless steel its unique properties is the specific combination of elements in its composition. The type and amount of each element decide how the steel behaves in different conditions. In this article, we explain what stainless steel is made of, how it is classified by composition, and how each type suits different applications.
What is the composition of stainless steel?
At its core, stainless steel is made from iron and a minimum of 10.5% chromium. The chromium forms a thin layer on the surface, which protects the metal from rust. But that’s not all. Depending on the grade, it may also include nickel, molybdenum, manganese, carbon, and other elements. Each of these adds something—better strength, more flexibility, or resistance to chemicals and heat.
Common elements found in stainless steel:
- Chromium
- Nickel
- Molybdenum
- Titanium
- Silicon
- Sulfur
- Manganese
- Phosphorus, etc.
According to its composition, stainless steel is divided into the following types:
- Austenitic stainless steel
- Ferritic stainless steel
- Martensitic stainless steel
- Duplex stainless steel
Note: The composition of stainless steel is what makes it unique and often the preferred choice for making outdoor fittings and structures, especially steel railing balcony and gates designs.
Stainless steel composition: Popular grades
Here are some popular grades of stainless steel and their compositions.
Austenitic stainless steel
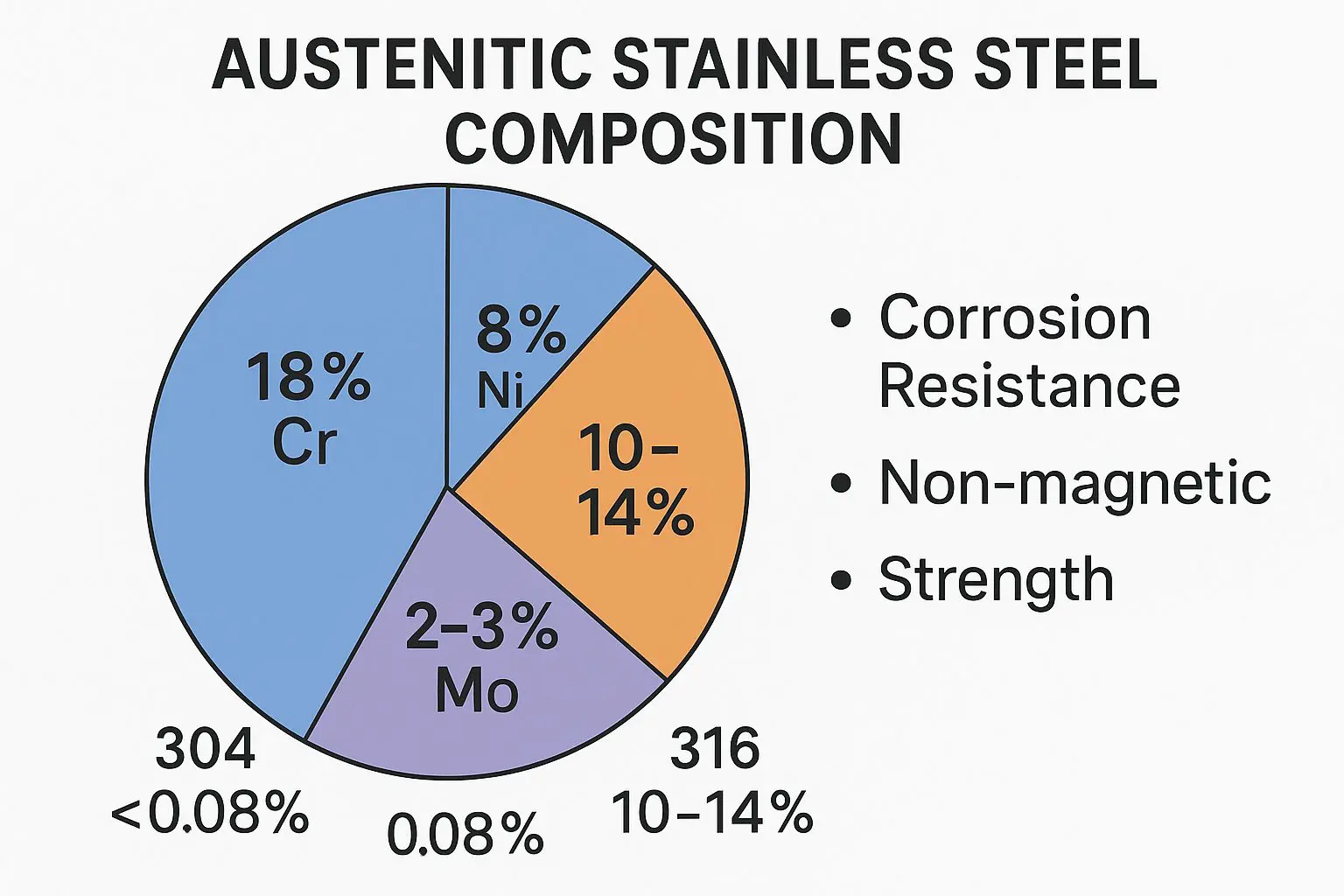
Austenitic stainless steel is one of the most commonly used types due to its excellent corrosion resistance and formability. It typically contains about 16% chromium and 6% nickel. The addition of nickel helps enhance its strength and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for a variety of applications. This type of stainless steel is non-magnetic, making it ideal for environments where magnetism could interfere with operations.
304 austenitic stainless steel composition
The composition of 304 grade stainless steel includes 18% chromium and 8% nickel, while it also has about 0.8% carbon. It is also known as 18-8 stainless steel due to its composition (18% chromium and 8% nickel). Some of the key features of 304 austenitic stainless steel include corrosion resistance, ease of fabrication, ease of cleaning, aesthetics, etc. Thanks to these characteristics, 304 austenitic stainless steel is commonly used in:
- Tanks for storing a variety of liquids
- Food processing industries (breweries, milk production units, etc.)
- Kitchen appliances
- Chemical industry
- Heat exchangers, etc.
316 austenitic stainless steel composition
The composition of 316 grade stainless steel includes 16-18% chromium, 10-14% nickel, 2 to 3% molybdenum and some percentage of carbon. 316L stainless steel is the low-carbon version of the same grade. The 316 austenitic stainless steel is the second most widely used grade after 304 stainless steel. The composition of 316 stainless steel grade offers one of the key advantages i.e. better corrosion resistance to chlorides such as salt. As a result, 316 austenitic stainless steel turns out to be a material of choice in the coastal regions. Here are some of the common applications of the grade.
- Coastal architecture: steel railings, panels, etc.
- Stainless steel roofing solutions
- Chemical containers
- Food processing industry
- Labs & pharma equipment
- Medical equipment & implants, etc.
904 grade stainless steel
904 grade stainless steel is low-carbon stainless steel. This grade of stainless steel is resistant to stress corrosion cracking and crevice corrosion. The composition of 904 grade stainless steel offers formability, toughness and weldability.
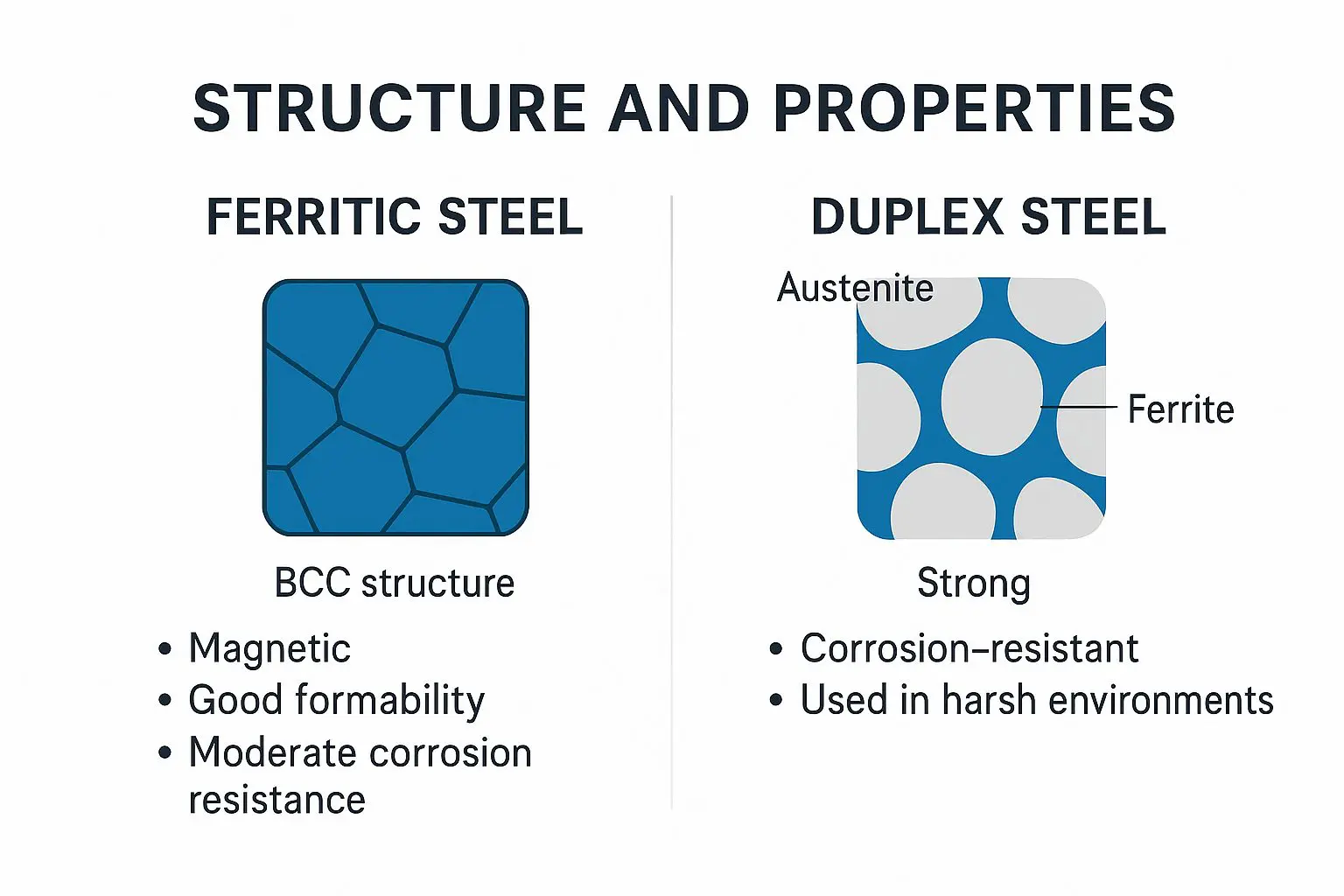
Ferritic stainless steel
The composition of ferritic stainless steel comprises a higher percentage of carbon as compared to austenitic stainless steel. The percentage of chromium ranges from 10.5% to 30%.
430 ferritic stainless steel composition:
430 stainless steel grade is one of the popular grades in the ferritic stainless steel family. The composition comprises a high level of chromium. Since it features good corrosion resistance and formability. The composition of 430 stainless steel grade has mechanical properties, which make it ideal for chemical applications. It is resistant to nitric acid too. Applications of 430 ferritic stainless steel include kitchen appliances, automotive, trims, etc.
434 ferritic stainless steel compositions
434 ferritic stainless steel is known to be non-hardenable. The composition of 434 ferritic stainless steel includes chromium, molybdenum, carbon, etc. The composition makes it an ideal choice for various industries including architecture, automotive, etc. Things such as furnace combustion chambers, dishwashers, gas burners, and so on.
Duplex stainless steel
Duplex stainless steel has a mix of ferrite and austenite types of stainless steel. The composition of duplex stainless steel comprises of very high content of chromium i.e. about 21-25% it also contains around 5% molybdenum. The composition of duplex steel makes it corrosion resistance and tough. As a result, duplex stainless steel is ideal to be used in chemical, oil and gas, marine, shipping industries, etc.
One of the popular grades of duplex stainless steel is 2205. Typically, the composition of 2205 duplex stainless steel is 22% Chromium and 5% Nickel.
The Role of Alloying Element
By now we know that what makes every grade of stainless steel different is alloying elements. Each element has its own advantages. Here is a guide on what features each element adds to stainless steel.
- Chromium: Chromium is an important element as stainless steel is defined by the minimum 10.5% of chromium. A higher percentage of chromium prevents steel corrosion.
- Nickel: Nickel enhances formidability while it also increases strength and corrosion resistance.
- Carbon: Generally, stainless steel has lower carbon content. This is because a higher level of carbon means higher chances of corrosion. On the other hand, carbon content increases the strength of stainless steel.
- Molybdenum: Molybdenum is known for increasing resistance to atmospheric corrosion.
- Nitrogen: Nitrogen offers protection against pitting corrosion.
Also read: Steel and stainless steel utensils – Business opportunities in India
Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Composition for Your Project
When selecting stainless steel for any project, it’s important to take a step-by-step approach that considers both technical needs and practical limitations.
Start with Your Requirements
Begin by clearly identifying what your project involves. Consider the working environment — will the material face moisture, heat, chemicals, or physical wear? In industries like oil & gas, pharmaceuticals, or chemical processing, you’ll often need to stick to specific, certified grades due to strict safety and durability standards. But in general construction or fabrication, you might have more flexibility.
Look at What’s Easily Available
Next, see which grades of stainless steel are accessible through local suppliers. Local sourcing can often save time, reduce shipping costs, and simplify logistics — especially useful for urgent or large-scale jobs.
Compare and Make an Informed Choice
Don’t just go with the first quote. Speak to multiple vendors, ask for material test certificates if needed, and compare what they offer — not just in terms of cost, but also in grade, quality, and lead time. Choose the option that best fits your project’s priorities, whether that’s strength, corrosion resistance, budget, or delivery speed.
Conclusion
Choosing the right composition for stainless steel is not just about knowing the grades—it’s about aligning material properties with your project’s specific needs. Whether your priority is corrosion resistance, strength, formability, or cost-efficiency, each alloying element brings its own advantage to the table. By understanding the role of these elements and evaluating factors like environmental conditions, availability, and budget, you can make an informed decision that ensures long-term performance and value. With the right approach, stainless steel becomes more than just a material—it becomes a reliable foundation for quality and durability in your project.
Looking to procure steel?
Tata nexarc helps manufacturers, builders and MSMEs source certified steel products, compare prices, and choose the right grade as per IS codes—with complete traceability and procurement confidence.
FAQs
What is the difference between austenitic and ferritic stainless steel?
Can austenitic stainless steel be welded easily?
Why is 304 stainless steel considered food-safe?
304 stainless steel resists corrosion, is non-reactive, and doesn’t leach harmful substances, making it ideal for food-related applications.
How does the addition of molybdenum improve stainless steel?
Molybdenum enhances corrosion resistance, especially against chlorides like saltwater, making it ideal for marine and chemical environments.
What are the main advantages of using 316 stainless steel over 304?
Is austenitic stainless steel magnetic?
How does the carbon content affect the properties of stainless steel?
Higher carbon content increases strength but can reduce corrosion resistance. Lower carbon steels are better for welding and offer improved corrosion resistance.
What industries primarily use austenitic stainless steel?
Why is 304 stainless steel called 18-8 stainless steel?
It contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel, providing strength and resistance to corrosion.
What are the environmental impacts of producing austenitic stainless steel?
Swati is a passionate content writer with more than 10 years of experience crafting content for the business and manufacturing sectors, and helping MSMEs (Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises) navigate complexities in steel procurement, and business services. Her clear and informative writing empowers MSMEs to make informed decisions and thrive in the competitive landscape.