Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Steel Grades and Standards That Shape Mesh Quality — Rewritten for Human Flow
- Coating Choices: Galvanised, PVC, and Stainless Routes
- Cost Performance Matrix for Core Applications
- Supplier Qualification and Raw Material Traceability
- Lead Time Buffering and Seasonal Demand Planning
- Documentation and Quality Control Workflow
- Conclusion
Indian MSMEs seldom buy steel mesh just once; it anchors fencing, gabion baskets, and reinforcement on every new project. Selecting the wrong grade floods budgets with hidden costs—premature corrosion, weld failure, and GST credit delays. The real advantage lies in matching base steel, coating, and delivery terms to project risk, not chasing the lowest steel mesh price per kg.
Procurement teams face three sharp pressures: volatile raw‑steel rates, patchy vendor documentation, and lead‑time shocks during monsoon hauls. The following playbook tackles each pressure head‑on, showing how to balance tensile strength, zinc coating 275 gsm options, and batch heat number traceability without inflating landed cost.
Steel Grades and Standards That Shape Mesh Quality — Rewritten for Human Flow
Choosing the right wire for steel mesh is a balancing act, not a checklist tick. Start with the standards. IS 1566 compliance covers low‑carbon cold‑drawn wire, the workhorse for welded panels. Coastal jobs, on the other hand, lean on IS 280 standard for galvanized strands that resist sea‑spray corrosion. Skip these references, and you gamble on vendor promises instead of proven benchmarks.
A quick look at a wire gauge chart explains why budgets burst. Shift from 3 mm to 4 mm wire and material weight per square metre almost doubles. Yet most compound wall fencing never needs that extra muscle. A simple tensile strength test at 200 MPa confirms whether the lighter gauge will hold, saving cash for critical fixtures elsewhere.
Paperwork protects margin as much as steel does. Insist on batch heat number traceability that links every coil to its melt; a mill test certificate dated within the last month keeps numbers honest. Buyers who archive these PDFs find GST input credit processing smoother, because the invoice, the certificate, and the delivery note speak the same language.
Coating Choices: Galvanised, PVC, and Stainless Routes
Salt, smog, and stray chemicals chew through steel mesh faster than most budgets allow. Galvanised wire mesh, with zinc coating 275 gsm, handles everyday rain and dust in inland zones. PVC coated mesh adds a plastic skin that cushions against abrasion from moving feed in poultry cages. Stainless steel mesh resists coastal salt spray but commands a premium; teams often overlook the payback period when life‑cycle cost outstrips capital cost by two years.
Price is not the only factor, documentation delays can stall dispatches. Many buyers chase the lowest galvanized price and ignore certificate gaps that prove coating mass. A supplier who skips the salt‑spray test report leaves MSMEs exposed to premature rust claims. Here’s where many sourcing teams lose margin unknowingly: repaint cycles double labour spend before year three, erasing any upfront saving.
Use a simple two‑column calculator. Column A lists initial coat cost for galvanised, PVC, and stainless. Column B tracks repaint or replacement frequency across a five‑year window. The option with the lowest total outflow, not the cheapest invoice, wins. This model works better for batch buyers with high turnover who can negotiate rate contracts with staggered dispatch schedules timed to project phases.
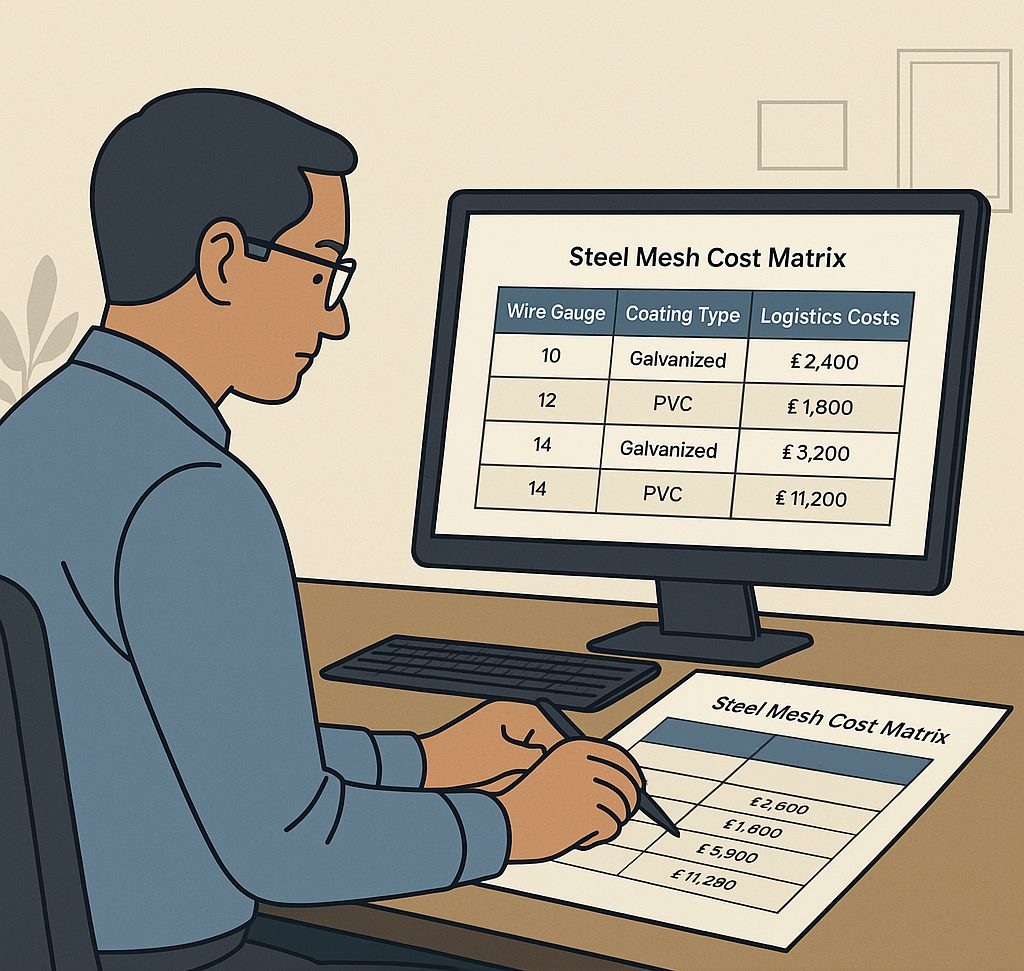
Cost‑Performance Matrix for Core Applications
Steel mesh rarely fails in a laboratory; it fails on dusty sites when the grade or coating is mismatched to real stress. A cost‑performance matrix forces buyers to weigh rupees against risk, converting kilogrames and gauges into square‑metre costs the finance team can track. Once the numbers sit side by side, the cheapest panel is often the most expensive decision over a five‑year window.
Compound Walls: Guarding the Perimeter
Perimeter fencing lives outdoors but faces modest load. A 3 mm galvanized panel, landed in western India, settles near ₹82 per square metre. Upgrading to 4 mm stainless steel mesh triples the invoice to roughly ₹210, yet the wall still shoulders only 15 kN. The matrix calls out the mismatch, steering buyers toward lighter wire with adequate zinc rather than costly alloy.
Gabion Baskets: Holding Back the Earth
Gabions endure water pressure and shifting soil. Here, tensile strength rules. Medium‑carbon welded wire mesh, backed by an IS 1566 certificate, delivers the pull without overspending on exotic coatings. Include hydrostatic load in the matrix; it shows that an extra millimetre of wire saves future rebuilds that can swallow twice the material budget.
Poultry Cages: Fighting Ammonia Fumes
Ammonia turns ordinary zinc dull and brittle. PVC coated mesh, although pricier upfront, resists chemical attack and keeps cage panels straight. The cost‑performance grid reveals that repaint labour alone, when spread across three years, outweighs the original premium of the coated panel.
Tracking the Hidden Rupees
Scrap removal, weld rework, and non‑returnable pallets seldom appear on quotations. Add them as a “shadow cost” column. The total often jumps ten percent, handing buyers fresh leverage for rate contract negotiation or staggered dispatch clauses.
Case Snapshot: Pune Walkway Project
A fabricator in Pune faced a walkway spec calling for 4 mm galvanized panels. The matrix flagged an alternative—3.15 mm wire with zinc coating 275 gsm—that met load limits and shaved eight percent off material spend. The freed cash funded stricter QC inspection, cutting site weld failures to near zero and delivering the project under budget.
Supplier Qualification and Raw Material Traceability
Indian buyers often lose more money to sloppy paperwork than to price escalation. A panel that looks perfect on arrival can still trigger non‑conformance reports if the heat number or invoice code is wrong. To avoid those traps, MSME sourcing teams need a step‑by‑step filter that screens suppliers, verifies raw‑material lineage, and keeps deliveries predictable even during peak season.
The checkpoints below translate that filter into practice. Each one tightens a different part of the supply chain—technical compliance, document hygiene, or logistics stability—so that no single weak link can derail the entire order.
Vendor Shortlisting: Looking Past the Brochure
Start with hard evidence, not marketing claims. Build a vendor qualification checklist that covers three pillars:
- Standards in place – Valid IS 1566 or IS 280 certificates, renewed within the last twelve months.
- Capacity on record – Galvanising output per month and weld‑mesh throughput, both backed by production logs.
- Delivery history – On‑time‑in‑full scores by pin code inside India’s hub‑and‑spoke logistics grid.
Vendors missing data in any column go to a “watch” list for future audits rather than today’s purchase order. This simple gate removes most of the late‑truck and under‑spec dramas that inflate landed cost.
Certificate Verification: Trust the Numbers, Not the Stamp
Batch heat number traceability is your warranty in a line of digits. The same number must appear on coil tags, mill test certificates, packing slips, and the final invoice. Cross‑checking takes ten minutes and blocks weeks of dispute if welds crack on site.
Reject certificates older than thirty days; those figures may describe steel stored in monsoon humidity, not material rolling out today. Fresh paperwork also speeds up GST input credit because the invoice, certificate, and HSN code align without manual edits.
Transit Reliability and Payment Terms
A perfect mesh panel is useless if it arrives a fortnight late. Ask each shortlisted supplier to share average door‑to‑door lead times for your district across summer, monsoon, and festival periods. Use that data to build a lead‑time buffer that cushions site schedules without padding inventory.
Cash flow matters just as much. MSMEs thrive on staggered terms such as 20 percent advance, 40 percent against proof of dispatch, and 40 percent after goods receipt. The split keeps vendors funded while protecting buyers from overexposure.
Dual‑Sourcing Without Inflating MOQ
Relying on one mill invites shutdowns when transport strikes or furnace repairs hit. A 70‑30 supplier split solves the risk:
- Primary mill – Handles bulk under a rate contract, locking in price.
- Regional stockist – Ships emergency volumes within forty‑eight hours.
Rotate the ratio each quarter based on service record. This light‑touch review keeps both suppliers competitive and trims MOQ optimisation headaches.
Field Example: Chennai Fabricator Steadies Its Supply Chain
A structural fabricator near Chennai missed a critical hand‑over because its sole supplier’s truck was stuck on a flooded highway. After that slip, the team adopted the dual‑sourcing model above. Bulk panels now leave a Raipur mill on fixed weekly slots, while a Tiruchirappalli stockist fills gap orders. In twelve months, on‑time delivery climbed from 76 percent to 93 percent, and weld‑failure claims dropped by half thanks to stricter certificate checks.
Lead‑Time Buffering and Seasonal Demand Planning
Indian projects rush in spurts. School walls, festival stages, and highway fences all demand steel mesh at the same time, then go quiet. Without a clear calendar, panels sit in a yard rusting or arrive after the concrete sets. A smart timeline links weather data, site milestones, and supplier capacity so mesh lands when crews need it, not when trucks find a slot.
Map the Calendar Before the RFQ
Begin with three data sets: historical monsoon onset by district, local festival peaks, and past supplier transit logs. Plot them on a simple Gantt. A cold look at the chart reveals two blackout windows—late July floods and October carnival closures. Circulate that chart with the RFQ template so bidders price in real transit days. The habit trims padding and leaves room for sharper rate contract negotiation.
Build a Dynamic Lead‑Time Buffer
Static buffers waste cash. Instead, set a sliding scale. When highways stay dry, a seven‑day cushion covers hub‑and‑spoke logistics into tier‑2 cities. As rain percentages climb, expand the buffer to twelve days for galvanized wire mesh and sixteen for heavier stainless steel mesh. Use a traffic light system in the ERP: green for normal, amber for alert, red for hold. Buyers who adjust in real time slash demurrage fees and avoid panic air freight.
Align Staggered Dispatch with Cash Flow
Large orders tie up working capital. Break them into three dispatches that match site progress. Dispatch one ships reinforcement mesh for early slab work. Dispatch two brings galvanized steel mesh for compound wall fencing. Dispatch three tops up any shortfall with PVC coated mesh or welded mesh panels depending on weather. Staggered schedules keep the lead‑time buffer active without stockpiling and improve MOQ optimization.
Monsoon Case: Ahmedabad Fabricator
An Ahmedabad fabricator missed two completion dates in 2023 when trucks stalled near Bharuch. The team rebuilt its calendar, flagging July to mid‑August as red. Orders for that period now leave the mill by early June. The result was that the on‑time delivery jumped from 68 percent to 94 percent, and overtime labour dropped by a quarter.
Documentation and Quality‑Control Workflow
Paperwork errors sting harder than rust. A single slip in the HSN block, and your GST money freezes. Miss a heat number, and the site supervisor hunts for replacements while labour clocks overtime. The cure is a tight chain that pairs every sheet with a matching physical check, long before the steel mesh rolls onto rebar.
Seal the Paper Trail Before Loading
Insist on a three‑way match process that ties purchase order, mill test certificate, and invoice into one story. Quantity, grade, and batch heat number must read exactly the same. Push back on any document carrying a stale signature date. Vendors who tidy their files early usually sharpen their prices later.
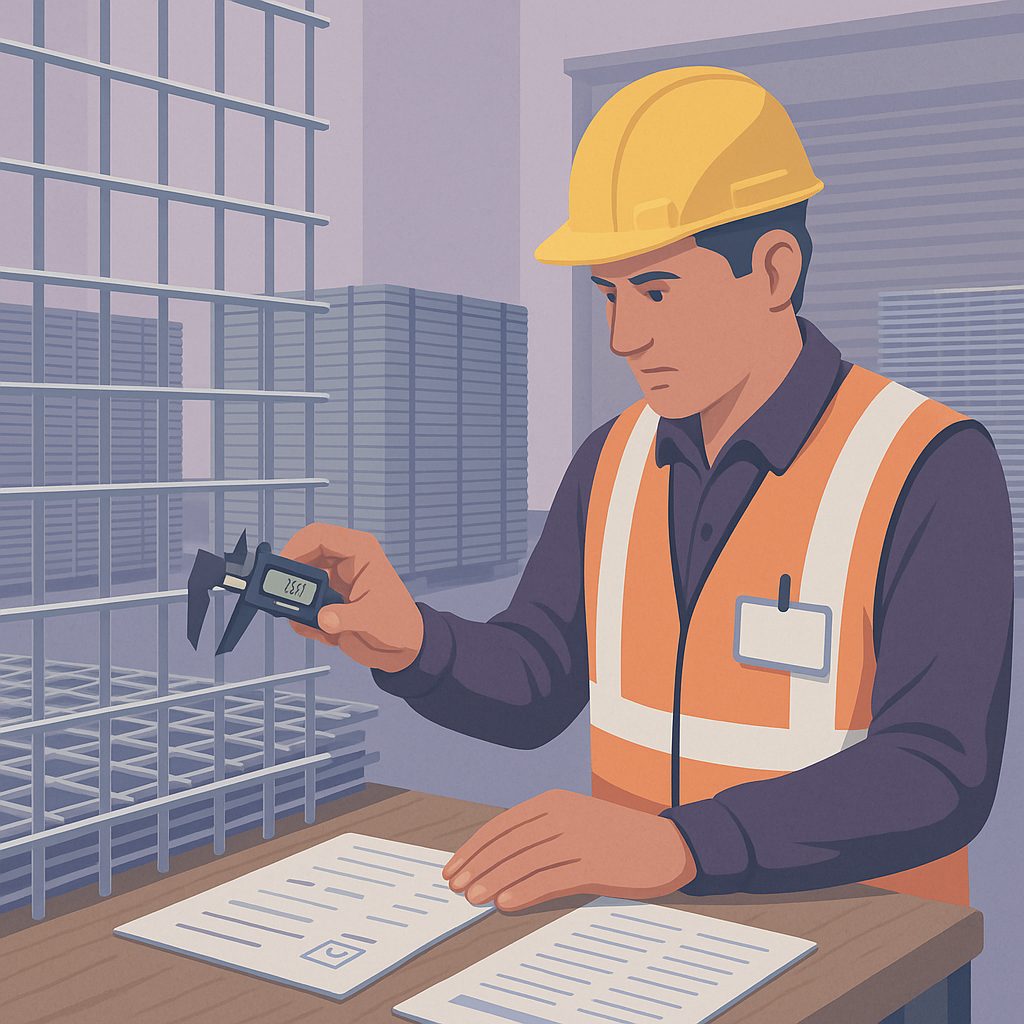
Catch Defects at the Gate, Not on the Wall
Unwrap the first panel from each bundle. Check wire gauge with a digital caliper; log weld spacing against the QC inspection checklist. Run a handheld tensile meter—twenty seconds tells you if the mesh meets code. Any reading outside tolerance earns a red tag that blocks the lot from production. It is cheaper to quarantine than to rebuild.
Time‑Stamped Proof Wins Disputes
Spot a zinc blister or a cracked weld? Photograph it on the spot. Embed the image and GPS stamp into an NCR email sent within four hours. Swift, visual proof flips the conversation from blame to resolution. Patterns of failure feed straight into the vendor scorecard, trimming bluff in the next negotiation round.
Surat Use Case: Money Unlocked, Quality Locked In
A Surat enclosure plant once bled weeks chasing GST refunds because invoices carried an extra zero in the HSN cell. After enforcing the match routine and gate checks, refund delays shrank to seven days. Weld rejects on incoming stainless mesh fell by one‑third, freeing staff to push production instead of paperwork.
Keep documents honest, inspections sharp, and evidence immediate. Do that, and steel mesh turns from a risk line into a controlled cost.
Conclusion
Good sourcing keeps projects safe, not just cheap. When steel mesh fits the load, carries the right zinc, and lands on time, margins stay intact. Every step above—grade checks, cost‑performance matrix, vendor qualification checklist, lead‑time buffer, and three‑way match—turns uncertainty into numbers a finance team can audit. Price is not the only factor; documentation delays can stall dispatches; knowing this helps buyers guard GST input credit and schedule alike.
Action list for the next RFQ cycle
- Attach the vendor qualification checklist and require fresh mill test certificates.
- Use the cost‑performance matrix to pick gauge, coating, and supplier split.
- Build a weather‑based lead‑time buffer; update it monthly.
- Enforce the three‑way match before trucks depart and run gate inspections on arrival.
Download the landed cost analysis sheet and the vendor scorecard template, share them across procurement, finance, and site teams, and watch rework disappear.
Looking to procure steel?
Tata nexarc helps manufacturers, builders and MSMEs source certified steel products, compare prices, and choose the right grade as per IS codes—with complete traceability and procurement confidence.
FAQs
Which steel grades are best suited for manufacturing welded steel mesh in India?
How does the choice of steel grade impact the lifespan of steel mesh?
What are the common steel defects that affect mesh quality?
Can recycled steel be safely used for steel mesh manufacturing?
What is the recommended zinc coating thickness for steel used in mesh panels for coastal applications?
How do you confirm the steel used in mesh panels matches the purchase order specification?
Does the source (integrated steel plant vs. mini-mill) affect the quality of steel for mesh?
What is the effect of wire drawing technique on the final mesh performance?
Are there sustainability standards or certifications for steel used in mesh production?
What laboratory tests should be done on steel before using it in mesh fabrication?
Ananya Mittal blends a background in data science with a passion for writing, contributing to Tata Nexarc’s efforts in creating insightful, data-informed content for MSMEs. Her work focuses on exploring sector-specific challenges and opportunities across procurement, logistics, and business strategy. She is also involved in leveraging analytics to strengthen content performance and deliver actionable insights to India's growing B2B ecosystem.