Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Specialty steel: A quick definition and why it matters for MSMEs
- Why specialty steel are growing faster than regular steel
- Key specialty steel segments driving India’s manufacturing future
- Specialty steel vs regular steel: What’s the business difference
- Where demand is coming from: Sector-wise breakdown
- Challenges MSMEs face when buying specialty steel
- Specialty steel sourcing checklist for MSMEs
- The future: Specialty steel will shape India’s industrial competitiveness
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
India’s manufacturing ecosystem is entering a phase where basic carbon steel is no longer enough. As the country targets becoming a global hub for EVs, electronics, aerosspace, defence, heavy engineering and precision manufacturing, the need is shifting rapidly from volume-based steel to value-added specialty steels.
Government initiatives such as the PLI scheme, import substitution missions, and growing export linkages have accelerated this shift. At the same time, OEMs across sectors – automotive, whitegoods, renewable energy, railways and defence – are demanding higher performance, greater compliance, and material traceability from their Tier-1, Tier-2 and Tier-3 suppliers.
This means one thing for Indian MSMEs:
Understanding about specialty steels is no longer optional but it has now become a commercial necessity.
From advanced high strength steels used in EV structures to precision flat products that are used in electronics and whitegoods. The new-age steel ecosystem is reshaping how businesses design, procure steel, and manufacture components. And SMEs that adopt these high-performance materials early, have a chance to gain better margins, stronger OEM relationships, long-term export readiness, etc.
This blog breaks down the specialty steels powering India’s manufacturing future – and what MSMEs must know to stay competitive in 2025 and beyond.
Specialty steel: A quick definition
Specialty steels are high-performance, engineered steel grades, and are designed for applications where regular carbon steel is not enough. In addition, specialty steel offer superior strength, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, electrical properties, formability, and precision. This, as a result, makes them essential for advanced manufacturing, unlike regular steel that are used in construction or generic fabrication.
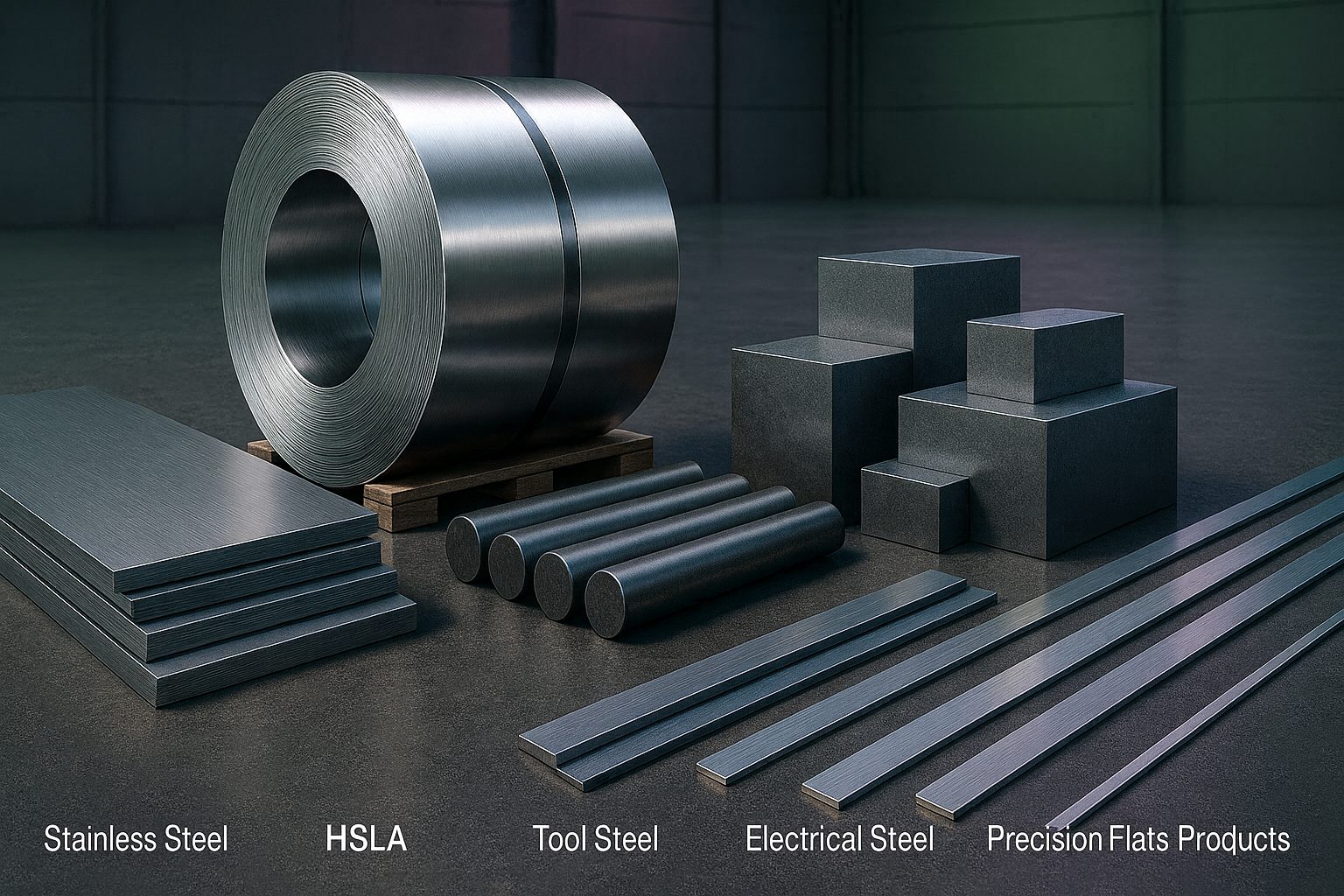
For Indian MSMEs, these types of steels generally include alloy steels, tool/ die steels, Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS), stainless steel (300/400 Series, Duplex), High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steel, electrical steel (CRGO/CRNO), heat-resistant/ wear-resistant steels, and precision flat products.
Why they matter for MSMEs
Apart from it, the demand for specialty steels is rapidly rising simply because manufacturing requirements today go beyond “just steel.” Consequently, OEMs expect:
- Higher performance (steel strength-to-weight, crashworthiness, corrosion resistance)
- Compliance and certifications [IATF, ISO, Production Part Approval Process (PPAP), traceability]
- Export-ready materials to meet global standards
- Lightweighting and energy efficiency for EVs and electronics
- Consistent quality for precision engineering
For MSMEs, this means specialty steels are not a premium choice anymore – they are the expected standard in high-growth sectors like EVs, aerospace, whitegoods, defence, medical devices, and renewable energy.
Why specialty steel are growing faster than regular steel
India’s steel consumption is no longer driven only by construction and infrastructure. Now-a-days, the fastest-growing demand comes from precision manufacturing. And regular steel can’t meet performance, compliance, export requirements, etc. Consequently, there is a direct shift towards specialty steels. And that too is expanding 2–3x faster than conventional carbon steel. A quick glance at the key drivers behind this rapid growth:
Precision manufacturing boom
Sectors including automotive, EVs, electronics, aerospace, medical devices, whitegoods, etc. requires raw material that have consistency, lightweighting, surface precision, and enhanced strength. All these features regular steel cannot offer.
Whether it’s EV crash structures, motor laminations, aerospace brackets, or medical components, specialty steels enable high accuracy and global-grade quality.
For MSMEs, this means customers increasingly demand components made from HSLA, AHSS, stainless, tool steel, and precision flats.
PLI scheme + PLI 2.0 (2025 policy update)
Next, government schemes such as PLI scheme has notable boosted demand for advanced steel categories. These include, tool/ die steel, electrical steel (CRGO/CRNO), coated and value-added steel, and automotive-grade steels.
As per latest, November 2025 update – consultations for PLI 2.0 are now prioritising:
• AHSS (Advanced High-Strength Steel)
• Auto-grade steel for EVs
• Electrical steel for motors/transformers
• Tool steel import substitution
This policy direction is pushing mills and service centres to expand domestic specialty capacity – directly benefiting MSMEs with better availability.
EV & advanced component manufacturing
The demand for EV is scaling rapidly in India. Thus, creating strong demand for:
- AHSS for crash components,
- HSLA for chassis,
- Electrical steel for motors,
- Stainless steel for battery enclosures, and
- Precision flats for stamped auto parts.
In addition, now MSMEs suppliers of EV from tier-2 and tier-3 now require strict OEM-approved materials to stay in the supply chain.
Defence and aerospace supply chain expansion
Growth in private manufacturing in defence and aerospace has been supported by initiatives such as Make in India. Also, defence indigenisation lists, and expansion of private tier-1 suppliers.
These sectors use large quantities of tool steel, alloy steel , AHSS, heat-resistant steels, etc. As a result, dependable long-term demand for specialty grades is generated
Renewable energy & green hydrogen growth
Wind turbine structures, solar trackers, hydrogen storage systems, electrolyser components, etc. rely on:
• HSLA,
• Duplex stainless steel, and
• Heat-resistant alloys.
Apart from it, the government’s hydrogen pilots and wind expansion plans in 2025 have accelerated this demand.
Tier-2/Tier-3 localisation push (2025 trend)
OEMs in auto, electronics, whitegoods and energy equipment are increasing localisation requirements.
This means more MSMEs must meet:
- Global-grade specifications
- Traceability and PPAP requirements
- Coating, flatness and surface standards
Further, the materials enabling this compliance are specialty steels – not basic carbon steels.
That means, specialty steels are growing faster as India’s manufacturing goals have moved beyond generic steel. Performance, certification, lightweighting and export readiness now drive real demand – and MSMEs that adopt these materials will stay aligned with OEM expectations and high-value supply chains.
Key specialty steel segments driving India’s manufacturing future
India’s move toward high-value manufacturing is creating strong, sustained demand for specific specialty steel categories. These segments are now the backbone of automotive, EVs, aerospace, electronics, defence, whitegoods and renewable energy supply chains – and MSMEs play a central role in processing, machining and fabricating these materials.
To understand in-detail, let’s have a practical, commercial breakdown of the most critical specialty steel categories that shapes the future:
Advanced High-Strength Steel (AHSS)
Uses:
Crash structures, BIW components, EV lightweighting, and high-strength automotive parts.
Why demand is rising?
OEMs need lighter yet stronger materials to meet safety standards and mileage/efficiency targets. Thus, AHSS is becoming mandatory in tiered automotive supply chains, which is especially for EVs.
MSME relevance:
Toolrooms, stamping units, and fabrication shops supplying auto OEMs increasingly need AHSS grades – often with PPAP and traceability requirements.
High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) steel
Uses:
Chassis, suspension parts, automotive frames, and high-strength structural components.
Why demand is rising:
It provides better strength without increasing thickness, thus, reducing weight and cost. With EV adoption rising and fuel efficiency norms tightening, HSLA is now considered a mainstream requirement
MSME relevance:
Fabricators, auto part manufacturers, and engineering shops use HSLA for improved strength-to-weight performance.
Electrical steel (CRGO/CRNO)
Uses:
Transformers, EV motors, power equipment, alternators, compressors.
Why demand is rising:
EV motor production and India’s massive power infrastructure upgrades need high-grade electrical steel. And also, demand is outpacing domestic supply.
Latest update (November 2025):
Government and SAIL are evaluating options for domestic CRGO production to reduce import dependence – signalling long-term market expansion.
MSME relevance:
Businesses that manufacture transformers, motors, EV powertrain parts, energy equipment, etc. rely heavily on this segment.
Tool and die steel
Uses:
Cutting tools, dies, moulds, punches, CNC tooling, extrusion tools.
Why demand is rising:
Toolrooms – largely MSME-driven – supply every major manufacturing sector. As OEMs demand better precision and longer tool life, demand for high-performance tool steel is rising.
MSME relevance:
Core category for toolrooms, die shops, CNC workshops, and component makers who rely on wear-resistant, heat-treatable grades.
Stainless steel (304L, 316L, Duplex, Super Duplex)
Uses:
Pharma, chemical, food processing, defence, marine, hydrogen, railways.
Why demand is rising:
Hygiene, corrosion resistance, pressure performance, and export certifications are now standard requirements.
2025 trend:
Stainless steel prices remain range-bound due to stable nickel supply. But, 316L and duplex grades continue to see strong uptick.
MSME relevance:
Usually, these grades are relied upon by fabricators, process equipment makers, pressure vessel manufacturers, cleanroom-component MSMEs, etc.
Wear-resistant and heat-resistant steels
Uses:
Mining machinery, heavy equipment, crushers, furnace interiors, cement plants.
Why demand is rising:
Infrastructure, mining capex, foundry expansion, etc. have directly increased demand for such grades.
MSME relevance:
These grades are used by machine shops, mining-equipment fabricators, and casting and heat-treatment businesses for high-durability parts.
Precision Flat Products
Uses:
Auto stampings, electronics casings, whitegoods, EV connectors, and battery components.
Why demand is rising:
Strict standards for surface finish, flatness, and gauge tolerance must be met – and they are achieved only through precision flats.
MSME relevance:
Sheet metal MSMEs serving auto, whitegoods and electronics OEMs depend on this category for high-quality stamping and fabrication.
Specialty steel vs regular steel
For many Indian MSMEs, the biggest confusion is simple: “Why should I pay more for specialty steel when regular steel is cheaper?” The answer is that specialty steel is not just another raw material – it is a performance enabler, an OEM requirement, and a quality assurance layer that directly impacts margins, approvals, rejection rates, and even export eligibility. The table below shows how regular steel and specialty steel differ in real business terms.
| Business factor | Regular steel | Specialty steel | MSME impact |
| Price | Low-cost, suitable for basic fabrication and low spec uses | Higher due to alloying elements and controlled processing, but delivers better lifecycle value | Lower rejections, smoother machining, longer tool life (saves money long-term) |
| Performance | Varies by batch; suitable for simple structures | Engineered for strength, corrosion/heat resistance, magnetic properties, surface accuracy, lightweighting | Better consistency and easier customer approvals |
| Applications | Construction, general fabrication, basic engineering | Automotive, EVs, aerospace, transformers, precision components, export-grade products | Entry into high-value supply chains with better margins |
| Value Addition | Limited; commodity-driven | Enables design optimisation, thickness reduction, longer part life, superior finish | Positions MSMEs as precision manufacturers |
| Buyer Demand | Mostly domestic infra and fabrication | Required by OEMs, global suppliers, high-performance industries | Stable demand from premium and export buyers |
| Certification | Minimal; often no formal approvals | Requires OEM approvals, PPAP, IATF, MTC validation, traceability, controlled heat treatment | Builds quality credibility and long-term buyer relationships |
Where demand is coming from?
Specialty steel demand in India has accelerated sharply in 2025. And it is driven by sectors requiring higher strength, tighter tolerances, corrosion resistance, global-grade certifications, light weight, etc. And thus, for businesses this shift is reshaping tooling setups, purchase preferences, and OEM qualification requirements.
Below is the most accurate and current view (as of Nov 2025) of where real demand is coming from:
| Sector | Key grades used | What’s driving demand (2025) | MSME takeaway |
| Automotive & EV Manufacturing | AHSS, HSLA, precision flats, electrical steel, tool steel | High EV adoption; crash + lightweighting norms; component localisation; motor, inverter & drivetrain production | OEM-approved specialty grades are mandatory across auto supply chains |
| Aerospace & Defence | Alloy steel, tool steel, heat-resistant steel, duplex stainless | Private aerospace part manufacturing; defence indigenisation; exports; growth of machining clusters | Predictable demand for precision machining & toolroom components |
| Power Equipment & Electrical Machinery | CRGO/CRNO, precision stampings, tool steels | EV charging infra; transformer upgrades; motor manufacturing; energy efficiency norms | Electrical steel is among 2025’s fastest-growing categories; domestic CRGO exploration underway |
| Whitegoods, Appliances & Consumer Electronics | Precision flats, coated steels, stainless steel | PLI momentum; localisation of components; rising Tier-2/3 consumption; high-accuracy enclosure needs | Precision flats are critical for stamping and high-finish parts |
| Medical Devices & Pharma Engineering | 304L, 316L, precision flats, corrosion-resistant grades | Cleanroom, process equipment, export-driven demand | Stable year-round demand with high compliance requirements |
| Oil & Gas, Heavy Engineering, Mining | Wear-resistant steel, heat-resistant alloy steel, corrosion-resistant grades | Pipeline upgrades; infra capex; refinery expansions | Specialty materials are essential for fabricators & EPC subcontractors |
| Data Centers | Stainless steel, HSLA, precision flats, coated steel | AI + cloud boom; hyperscale data center parks; precision cooling systems | One of the strongest new steel-consuming sectors with repeat orders |
| Green Hydrogen | Duplex stainless, high-pressure steels | Hydrogen pilot plants; electrolyser & storage equipment manufacturing | Still niche but fast-growing; high margins |
| Railways & Vande Bharat Ecosystem | AHSS, HSLA, corrosion-resistant stainless, precision flats | Rolling stock expansion; premium passenger systems; localisation norms | Specialty grades critical for structural + aesthetic components |
| Battery Cell & Advanced Energy Storage | Precision flats, stainless, nickel-rich specialty alloys | PLI-ACC manufacturing scale-up; domestic battery production | Growing demand for high-precision materials |
| Robotics, Automation & Industrial Machinery | Tool steel, alloy steel, high-strength steels | Automation in MSMEs; robotics & material handling manufacturing | High-strength steels and tool steels now core inputs |
Challenges MSMEs face when buying specialty steel
Mostly businesses benefit from specialty steel, but the buying process is not always easy. And the common issues include like limited supply, higher costs, approvals, longer delivery, etc.
These challenges often determine whether a business can qualify for OEM contracts or sustain production without delays.
Limited domestic suppliers for niche grades
AHSS, CRGO, tool steels, duplex stainless, heat-resistant alloys, are some of the grades that are not widely produced locally. Thus, businesses often depend on imports or stockists, that help reduces choice and increases waiting time.
High Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs)
Mills and importers usually supply specialty steel in fixed batch sizes. And, oftentimes the order quantities are high, and steel coil width options are limited. This, as a result, can push businesses to buy more than required quantity or alternatively source through service centres at a higher cost.
Longer delivery times
Imported grades such as electrical steel, tool steel and certain stainless types may take 45–90 days to arrive. In addition, customs checks can also add more time. This, makes urgent orders difficult and as a result delay production.
Dependence on imported Alloys
In India, alloys are still imported and finished steel for tool steel, electrical steel, high-end stainless and precision flats. And when prices fluctuate due to global nickel, molybdenum, chromium and vanadium markets, this consequently affects budgeting.
Documentation and approval requirements
Most clients require traceability, PPAP documents, IATF-aligned processes, controlled heat treatment, batch Mill test Certificates (MTCs). And business owners who fail to provide these systems may face rejections or may also lose eligibility for certain contracts.
Higher working capital
Specialty steel costs more than regular steel. And often businesses require more funds to maintain stock or buy multiple grades. This, as a result, puts pressure on cash flow if credit support is limited.
More checks on imported material
As per recent updates, now there has been increased checks on BIS certification, chemical composition, paperwork for imported alloy-rich grades, and so on. This further adds extra work for MSMEs that depend on imports.
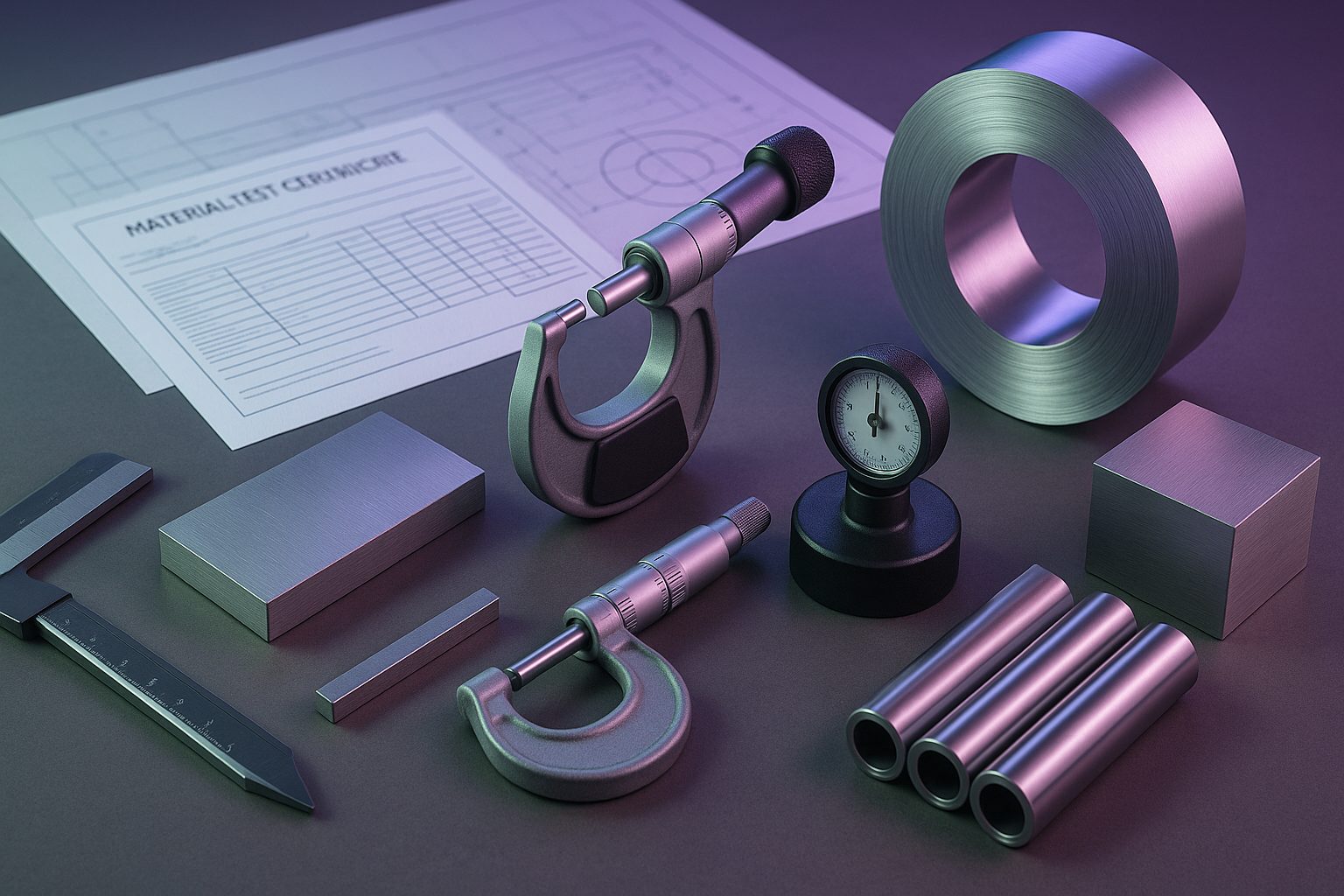
Specialty steel sourcing checklist for MSMEs
Specialty steel procurement is does not mean how to buy raw material. However, it is also about ensuring grade accuracy, performance reliability, and downstream compliance. As even a single mismatch in chemical composition, surface finish, heat-treatment condition, and so on, can lead to rejections, tooling damage, or production delays.
So, to understand better, we have discussed more in-detail below so that businesses can source specialty steels with confidence and avoid common costly mistakes:
Verify grade and sub-grade specification
You can confirm the exact grade (for instance, 316L vs 316, HSLA vs AHSS) and sub-grade variations required for your application. OEM drawings often specify:
- Yield strength
- Tensile properties
- Coating or condition
- Thickness tolerance
However, do note that a single misinterpretation can lead to non-conformance.
Check Chemical Composition & Mechanical Properties
Ensure the material meets the required:
- Alloying element ranges (Cr, Ni, Mo, Nb, V, etc.)
- Yield and tensile strength
- Elongation
- Hardness
- Impact properties (if applicable)
You should always request comparative test reports when buying from new suppliers.
Confirm the Mill Test Certificate (MTC) and batch traceability
MTCs should include:
- Heat number
- Chemical composition
- Mechanical test results
- Standards followed
- Mill location and production process
So, do remember that traceability is critical for auto, EV, aerospace and whitegoods OEM audits.
Verify OEM or vendor approval requirements
Some sectors require:
- OEM-approved mills
- PPAP Level 3 documentation
- Process capability (Cp/Cpk)
- Compliance with IATF/ AS9100 standards
Buying non-approved material may lead to outright rejection.
Match surface finish & flatness specifications
Especially important for:
- Precision flats
- Auto stampings
- Electronics enclosures
- Whitegoods parts
Thus, always check for surface roughness, oil coating if required, galvanised/coated layer thickness, edge burrs condition, gauge tolerance.
Confirm heat-treatment condition
Different applications require distinctly processed raw materials such as annealed, normalised, quenched and tempered (Q&T), solution-annealed (for stainless), incorrect heat-treatment condition which consequently leads to machining problems and part failures.
Validate packaging, handling & storage standards
Specialty steels are sensitive to:
- Moisture
- Scratches
- Coil damage
- Bending stresses
Insist on:
- VCI packing
- Corner protectors
- Export-grade pallets
- Protective films (for precision flats or stainless)
Well-packed material reduces rejection and improves yield.
The future: Specialty steel will shape India’s industrial competitiveness
The future: Specialty steel will shape India’s industrial competitiveness
India’s manufacturing strategy is rapidly shifting from capacity-led growth to capability-led growth. As the country strengthens its presence in automotive, EVs, defence, aerospace, electronics, renewable energy and precision engineering, specialty steels surely play a decisive role in evaluating product quality, export readiness, and global supplier acceptance.
There are multiple structural trends that make specialty steels central to India’s industrial future. These include:
India is moving from volume to value
Rather than competing on low-cost, commoditised steel, India is now focusing on:
- High-strength automotive steels
- Electrical steels for motors and transformers
- Precision strip products
- Tool and die steels for advanced fabrication
- High-performance stainless and alloy steels
This shift, as a result, increases industry value and also positions India in global high-precision supply chains.
Specialty steels enable export competitiveness
Export markets demand strict compliance on:
- Strength
- Corrosion resistance
- Surface finish
- Dimensional accuracy
- Traceability
Specialty steels help MSMEs meet global specifications and participate in export-led sectors like auto components, electronics, aerospace parts, and machinery.
EVs, hydrogen and renewables are creating new material standards
Now emerging technologies require:
- AHSS & HSLA for lightweighting,
- CRGO/CRNO for motors and power equipment,
- Duplex stainless for hydrogen systems, and,
- Precision flats for battery and EV electronics
Hence, these sectors can’t operate on regular steel, and specialty steels are foundational.
OEM supply chains are becoming more performance-driven
OEMs across auto, aerospace, whitegoods and electronics are tightening requirements around:
- Material grades
- Tolerances
- Coatings
- Heat treatment
- Testing
- Traceability
MSMEs using specialty steels gain a structural advantage in meeting these demands.
Technology, PLI incentives and domestic capacity are improving access
With mills upgrading to AOD, VIM, VAR, PLI-supported lines:
- Domestic production of high-grade steel is rising,
- Lead times for specialty steel will improve,
- Import dependence will gradually reduce, and even,
- Businesses will gain better access to consistent quality.
As a result, it supports India’s transition to a more engineering-led manufacturing economy.
Early adopters among MSMEs will gain long-term benefits
Businesses that adopt specialty steels are more likely to:
- Win OEM vendor approvals,
- Reduce rejection and rework,
- Improve machining performance,
- Enter export-ready supply chains, and also
- Build long-term customer relationships.
The shift to specialty steels is not just a market trend but it’s a competitiveness strategy.
Conclusion: The specialty steel wave is already here – MSMEs must prepare now
Conclusion: The specialty steel wave is already here – MSMEs must prepare now
India’s manufacturing landscape is changing faster than ever. As sectors like EVs, aerospace, electronics, defence, power equipment, renewable energy and heavy engineering scale up, specialty steels have become the material backbone of this transformation. On the contrary, regular carbon steel does not support the performance, safety, compliance or export standards these industries demand.
Consequently, this shift for MSMEs becomes both a challenge and a massive opportunity.
And businesses that understand specialty steel grades, build sourcing discipline, strengthen certifications, and align with OEM-approved suppliers will ultimately secure stable, high-value, long-term work. Thus, those who delay this adoption may risk losing relevance in supply chains that are rapidly becoming more precision-driven and compliance-led.
Hence, it can be said that specialty steels are not just advanced materials – they are the foundation of India’s next decade of industrial competitiveness.
MSMEs that act today will be the preferred suppliers of tomorrow.
FAQs
How can MSMEs reduce scrap when using specialty steel?
Can specialty steel grades be mixed within one assembly?
How do MSMEs check if specialty steel is genuine?
Can MSMEs substitute AHSS with HSLA to save cost?
Do specialty steels have shorter or longer shelf life?
Are BIS certifications mandatory for all specialty steel grades?
Can specialty steel be laser-cut without distortion?
Does specialty steel require pre-processing before stamping?
Can imported specialty steel be used without OEM approval?
Do tool steels require re-hardening after machining?
Is domestic specialty steel quality comparable to imported grades?
What is the biggest risk when buying specialty steel from local traders?
Charul is a content marketing professional and seasoned content writer who loves writing on various topics with 3 years of experience. At Tata nexarc, it has been 2 years since she is helping business to understand jargon better and deeper to make strategical decisions. While not writing, she loves listing pop music.