Table of Contents
Introduction
In 2026, the EPC tender process has become stricter and more system driven. For MSMEs, entry into government EPC tenders India depends on documentation discipline as much as technical strength. Price alone rarely decides qualification.
The EPC tendering process in India screens bidders at multiple stages. Errors during upload or eligibility mismatch can stop the EPC bid submission process before financial bids open.
What makes it different from standard supply tenders
The infrastructure tender process India for EPC contracts involves deeper scrutiny. Authorities review turnover, similar project experience, manpower details, and compliance declarations during EPC technical bid evaluation.
Many MSMEs treat EPC tender documents India like standard purchase tenders. That assumption leads to avoidable EPC bid rejection reasons.
Common early gaps in the EPC tender process
In real procurement cycles, small lapses create major setbacks. Common issues include:
• Expired statutory registrations during submission
• Incorrect understanding of EPC EMD requirements
• Missing annexures in the EPC bid documentation checklist
• Ignoring EPC compliance requirements in risk clauses
These gaps do not reflect capability weakness. They reflect preparation gaps.
This guide explains how the EPC tender process works in India, what EPC tender eligibility criteria demand, and how MSME participation in EPC tenders can improve through structured planning.
What is the EPC tender process in India?
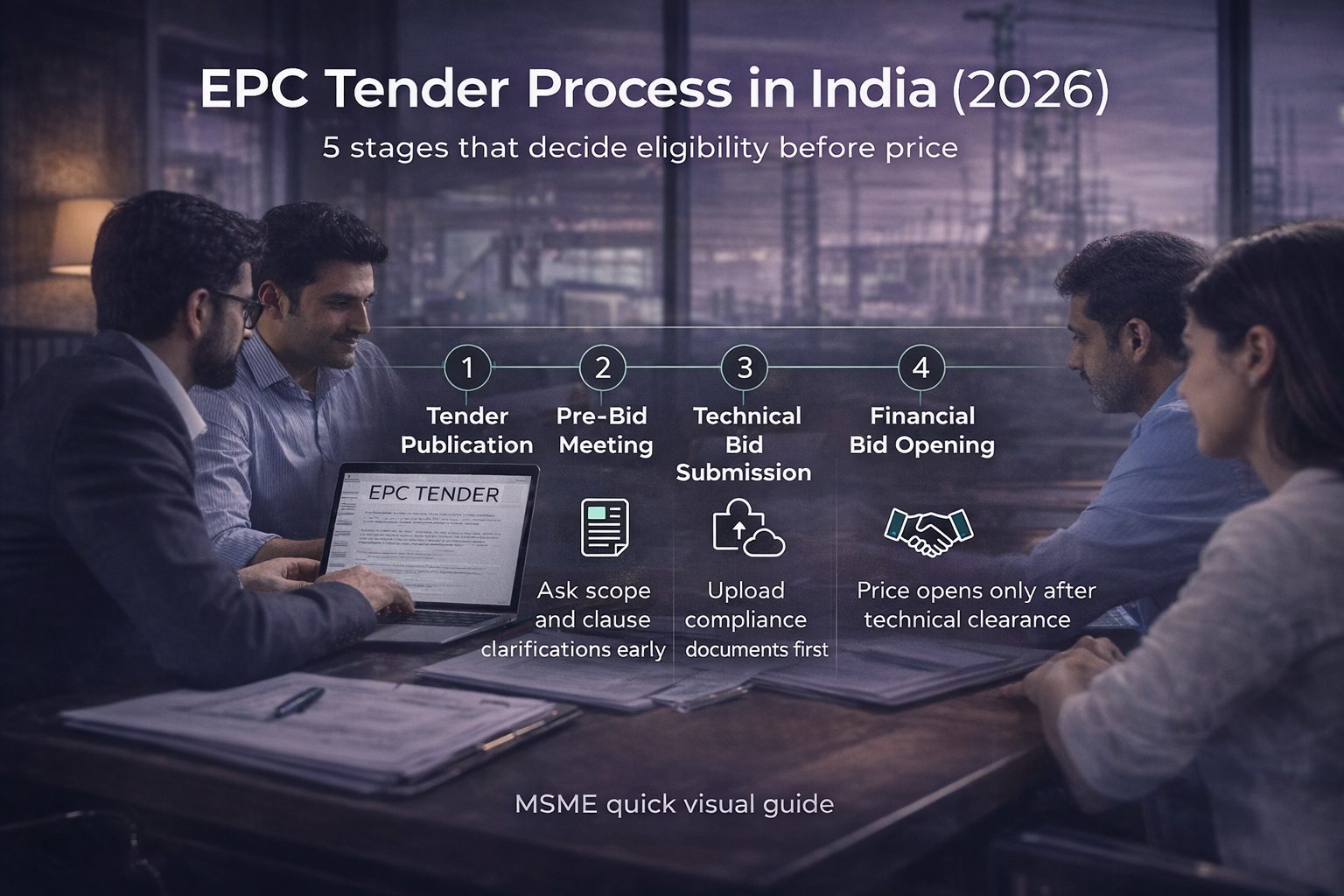
The EPC tender process follows a structured sequence. Each stage filters bidders on compliance, capability, and financial strength. Missing one requirement can end participation early.
The turnkey project tender process in India typically moves through defined milestones. Understanding the flow helps MSMEs plan documents and bank arrangements in advance.
Stage 1: Tender publication
Authorities publish government EPC tenders in India on central or state e-procurement portals. The notice includes scope, estimated value, timelines, and EPC tender eligibility criteria.
At this stage, firms should review qualification norms instead of rushing to download the BOQ. Early screening saves time and cost.
Stage 2: Pre-bid meeting process
The EPC pre-bid meeting process allows bidders to seek clarification on scope, specifications, or commercial clauses.
Serious bidders attend with prepared queries. Clarifications issued after this stage become part of the final EPC tender documents India.
Stage 3: Technical bid submission
During the EPC bid submission process, technical documents are uploaded first. Authorities conduct EPC technical bid evaluation to verify compliance with eligibility and documentation norms.
Common checks include:
- Turnover and net worth validation
- Similar project completion certificates
- Manpower and equipment declarations
- Compliance with EPC bid qualification norms
Only qualified bidders move forward.
Stage 4: Financial bid opening
After technical clearance, authorities conduct EPC financial bid opening. Pricing is compared only among technically accepted bidders.
In the EPC tender process, financial competitiveness matters only after compliance accuracy.
Stage 5: Contract award process
The EPC contract award process includes letter of intent issuance, performance bank guarantee EPC submission, and agreement signing.
Preparation across all stages reduces last minute risk.
EPC tender process in India – A quick go-to reference table
| Stage | What Happens | Key Actions for MSMEs | Helpful Portal/Resource |
| Tender Publication | Tenders are announced | Check eligibility before download | https://eprocure.gov.in |
| Review EPC tender eligibility criteria | https://etenders.gov.in | ||
| Pre-Bid Meeting | Clarifications on scope and terms | Prepare queries early | Tender notice document |
| Note addenda and clarifications | Portal notification section | ||
| Technical Bid Submission | Upload compliance documents | Ensure statutory registrations are valid | State e-Procurement portals |
| Follow EPC bid documentation checklist | NSIC, Udyam registry | ||
| Technical Evaluation | Authority verifies eligibility | Respond to queries promptly | Tender portal query feature |
| Track portal status dashboards | Portal status trackers | ||
| Financial Bid Opening | Only qualified bids are opened | Confirm pricing aligns with cash plan | Tender portal financial tab |
| Check EPC bid security rules India | Tender conditions section | ||
| Contract Award | LOI and performance guarantee | Prepare bank guarantee documents | RBI / Bank advisory pages |
| Complete vendor onboarding | Contract signing office |
Eligibility criteria in EPC tenders for MSMEs
Eligibility determines whether a bid is even opened. In the EPC tender process, qualification filters apply before pricing is reviewed. Many firms prepare commercial estimates first and study eligibility later. That sequence creates avoidable rejection.
Turnover and net worth requirements
Most government EPC tenders India specify minimum turnover over the last three financial years. Some also require positive net worth certification.
Authorities verify these figures during EPC technical bid evaluation. A mismatch between audited statements and uploaded declarations leads to immediate disqualification.
For MSMEs, conservative bidding within financial capacity protects credibility. Inflated participation without matching balance sheet strength rarely passes scrutiny.
Similar project experience criteria
EPC tender eligibility criteria usually demand completion of similar works within a defined value range. The definition of “similar” matters.
For example, a firm executing fabrication for industrial sheds may not qualify for a water treatment EPC package unless scope alignment is proven. Completion certificates must clearly mention project value and work description.
Many MSMEs overlook wording differences between “completed” and “substantially completed.” That distinction affects eligibility.
Technical manpower and equipment conditions
Tender authorities often ask for key personnel declarations and equipment ownership details. Infrastructure tender process India relies heavily on capacity proof.
Experience certificates for engineers, plant machinery lists, and lease agreements must match tender requirements exactly. Minor inconsistencies create EPC bid rejection reasons.
MSME exemptions and NSIC benefits
Certain EPC EMD requirements may allow exemption for registered MSMEs under specific conditions. NSIC registration and valid Udyam certification must remain active at submission stage.
However, exemptions do not remove compliance obligations. All other EPC compliance requirements still apply during the EPC bid submission process.
In the EPC tender process, eligibility accuracy is not a formality. It is the first approval gate.
Documents required for EPC tender submission
Documentation drives the EPC tender process. Even technically strong firms fail when paperwork does not match tender wording. The EPC bid submission process demands structured document control, not last-minute compilation.
Statutory and registration documents
Authorities expect valid statutory registrations during submission. These typically include:
- PAN and GST registration
- Udyam or MSME certificate
- NSIC registration, if claiming exemption
- Labour and industry related licences where applicable
Expired certificates remain one of the most common EPC bid rejection reasons. Many MSMEs overlook document expiry when uploading certificates.
Financial documents
Financial capacity must align with EPC tender eligibility criteria. Commonly required documents include:
- Audited balance sheets for the last three years
- Turnover certificate certified by a chartered accountant
- Net worth statement
- Bank solvency certificate, if specified
During EPC technical bid evaluation, authorities compare uploaded figures with declared values. Inconsistency leads to disqualification.
Technical and experience documents
EPC tender documents India usually require:
- Completion certificates of similar works
- Work order copies
- Detailed project descriptions
- Key personnel CVs and deployment plan
- Equipment ownership or lease proof
The scope description in completion certificates must match eligibility clauses. Broad certificates without value mention often fail scrutiny.
Bid security and EMD requirements
The EPC bid submission process also includes compliance with EPC EMD requirements and EPC bid security rules India.
If exemption is claimed, supporting documents must be uploaded correctly. If EMD is required, payment mode and timing must match portal instructions.
In the EPC tender process, documentation discipline determines qualification before price comparison begins.
Step-by-Step EPC bid preparation checklist
The EPC tender process rewards preparation done before the portal opens. Many MSMEs begin compiling documents a few days before submission. That approach increases risk. A structured EPC bid checklist for MSMEs reduces last-minute errors.
Step 1: Pre-qualification screening
Before downloading the BOQ, review EPC tender eligibility criteria carefully. Check turnover thresholds, similar project value, and technical manpower requirements.
If any condition does not align, reconsider participation. Submitting an ineligible bid affects credibility in future government EPC tenders India.
Step 2: Document verification
Create an internal EPC bid documentation checklist. Verify that:
- All statutory registrations are valid
- Completion certificates match required scope
- Financial figures match audited statements
- NSIC or MSME exemption documents are current
In real procurement cycles, small mismatches lead to technical rejection.
Step 3: Commercial term review
Do not focus only on rates. Review EPC tender documents India for risk clauses. Pay attention to:
- EPC compliance requirements
- Liquidated damages clauses
- Performance bank guarantee EPC percentage
- Payment milestone structure
Risk often hides in commercial terms, not in the BOQ.
Step 4: Portal submission validation
Follow EPC portal submission guidelines strictly. Upload documents in correct formats and categories. Confirm digital signatures are active.
Before final submission in the EPC bid submission process, recheck document attachments and acknowledgement receipts.
A disciplined checklist improves MSME participation in EPC tenders and reduces avoidable EPC bid rejection reasons.
Common mistakes in the EPC tender process
The EPC tender process eliminates bids for reasons that are often preventable. Most rejections do not happen because of pricing errors. They happen because compliance steps were rushed or misunderstood.
Misreading eligibility clauses
Many firms skim EPC tender eligibility criteria and assume similarity in past work. However, wording matters. “Similar nature of work” may refer to scope, value, or sector.
During EPC technical bid evaluation, authorities compare certificates strictly against tender language. Even small scope mismatches can lead to rejection.
Incomplete or incorrect uploads
The EPC bid submission process requires uploading documents in specific folders and formats. Missing annexures, unreadable scans, or unsigned declarations remain common EPC bid rejection reasons.
Portal acknowledgements must be checked before deadline closure. In real procurement cycles, submission timing matters more than last-minute corrections.
Overlooking EMD and bid security rules
EPC EMD requirements and EPC bid security rules India must match exactly with tender instructions. Incorrect payment mode or delayed transaction invalidates the bid.
Claiming MSME exemption without valid NSIC or Udyam documentation also leads to disqualification.
Ignoring risk clauses during review
Some bidders focus only on pricing and skip EPC commercial terms review. EPC compliance requirements, liquidated damages, and performance bank guarantee EPC conditions affect long-term exposure.
In the EPC tender process, qualification depends on discipline. Careful reading and timely preparation reduce unnecessary rejection.
What happens after you win the tender?
Winning a bid does not end the EPC tender process. It shifts responsibility from compliance to execution readiness. Many MSMEs underestimate this transition stage.
Letter of intent and acceptance
After EPC financial bid opening and final approval, the authority issues a Letter of Intent. The bidder must confirm acceptance within the specified timeline.
Delays at this stage can affect credibility in future government EPC tenders India.
Performance bank guarantee submission
The EPC contract award process usually requires submission of a performance bank guarantee EPC within a defined period.
Banks verify limits and format strictly. Incorrect guarantee wording or delayed submission can delay contract signing.
Agreement signing and documentation
Formal agreement signing follows guarantee submission. Contract copies, compliance declarations, and execution schedules are finalised.
Key personnel deployment plans and insurance documents may also be required before site mobilisation.
Mobilisation and kick-off
After documentation closure, mobilisation begins. Equipment movement, manpower deployment, and supplier coordination start as per schedule.
At this stage, financial discipline becomes critical. The gap between mobilisation expense and first certified bill affects cash flow.
In the EPC tender process, structured preparation before award ensures smoother transition into execution.
Conclusion
The EPC tender process in 2026 demands precision at every step. Eligibility screening, document control, portal submission, and risk review determine whether a bid moves forward. Pricing comes later.
For MSMEs, participation in government EPC tenders India should follow capacity assessment, not ambition alone. Careful review of EPC tender documents India, infrastructure tender eligibility criteria, and EPC compliance requirements reduces avoidable rejection.
In real procurement cycles, discipline builds reputation. Each correctly submitted bid strengthens qualification history, even if the contract is not won.
The EPC tender process rewards preparation, financial clarity, and attention to detail. Businesses that treat tendering as a structured compliance exercise position themselves for steady growth in large infrastructure and turnkey project opportunities.
Looking to procure steel?
Tata nexarc helps manufacturers, builders and MSMEs source certified steel products, compare prices, and choose the right grade as per IS codes—with complete traceability and procurement confidence.
FAQs
Can a company withdraw after submitting a bid in the EPC tender process?
How long does the EPC technical bid evaluation usually take?
Are digital signatures mandatory in the EPC bid submission process?
Can multiple bids be submitted for the same EPC tender?
Is site visit mandatory before participating in EPC tenders?
Can MSMEs correct documents after submission in the EPC tender process?
Do EPC tenders allow joint financial statements in consortium bids?
How are technical scores calculated in EPC tender evaluation criteria?
What happens if two bidders quote the same lowest price?
Are subcontractors evaluated during the EPC tender process?
Can EPC contracts be terminated after award?
Does previous bid rejection affect future EPC tender participation?
Charul is a content marketing professional and seasoned content writer who loves writing on various topics with 3 years of experience. At Tata nexarc, it has been 2 years since she is helping business to understand jargon better and deeper to make strategical decisions. While not writing, she loves listing pop music.