Table of Contents
Introduction
India’s infrastructure push continues across highways, metro rail, power transmission, and renewable energy. At the centre of this expansion sit EPC Projects in India, where one entity handles engineering, procurement, and construction under a single contract.
For policymakers, this structure improves accountability. For MSMEs, it concentrates responsibility and financial exposure. The opportunity is real, but so is the risk.
EPC in simple terms: EPC stands for Engineering, Procurement and Construction. In this model, one contractor usually takes responsibility for design, material procurement, execution, and project handover as per agreed scope.
For MSMEs, this sounds convenient, and in many cases it is. A single-point structure can reduce coordination effort, especially when internal technical teams are small.
What makes engineering procurement construction different
In Engineering Procurement Construction India contracts, the contractor carries design liability, material sourcing responsibility, and execution timelines. Payment depends on milestone completion. Performance guarantees remain active until handover.
Many MSMEs assume EPC projects in India operate like standard supply contracts. They do not. Documentation intensity, compliance sequencing, and technical scrutiny are significantly higher.
Where MSMEs usually enter
MSME participation in EPC projects rarely begins as a prime contractor. Entry typically happens through:
- Subcontracting in EPC projects under large EPC contractors in India
- Consortium bidding EPC India models to meet turnover thresholds
- Vendor registration for specific packages in turnkey infrastructure projects India
Each route requires careful study of EPC tender documents in India and infrastructure tender eligibility criteria India.
Common early mistakes
In real procurement cycles, timing often matters more than pricing. Several recurring issues appear in government EPC tenders India:
- Expired statutory certificates during portal submission
- Misinterpretation of EMD or NSIC exemption conditions
- Ignoring EPC contract risk allocation clauses
- Underestimating working capital for mobilisation advance EPC contract recovery
Also read: EMD Exemption for MSMEs & Startups in Government Tenders
These mistakes rarely reflect technical weakness. They reflect preparation gaps.
The sections ahead examine sector opportunities, the EPC bidding process in India, financial exposure, and EPC project financing realities. For MSMEs assessing EPC projects in India, structured planning remains the difference between participation and rejection.
Understanding the EPC model in India
Before bidding or partnering, MSMEs must understand how risk, responsibility, and payment structures operate within EPC Projects in India. The following comparison clarifies the key differences:
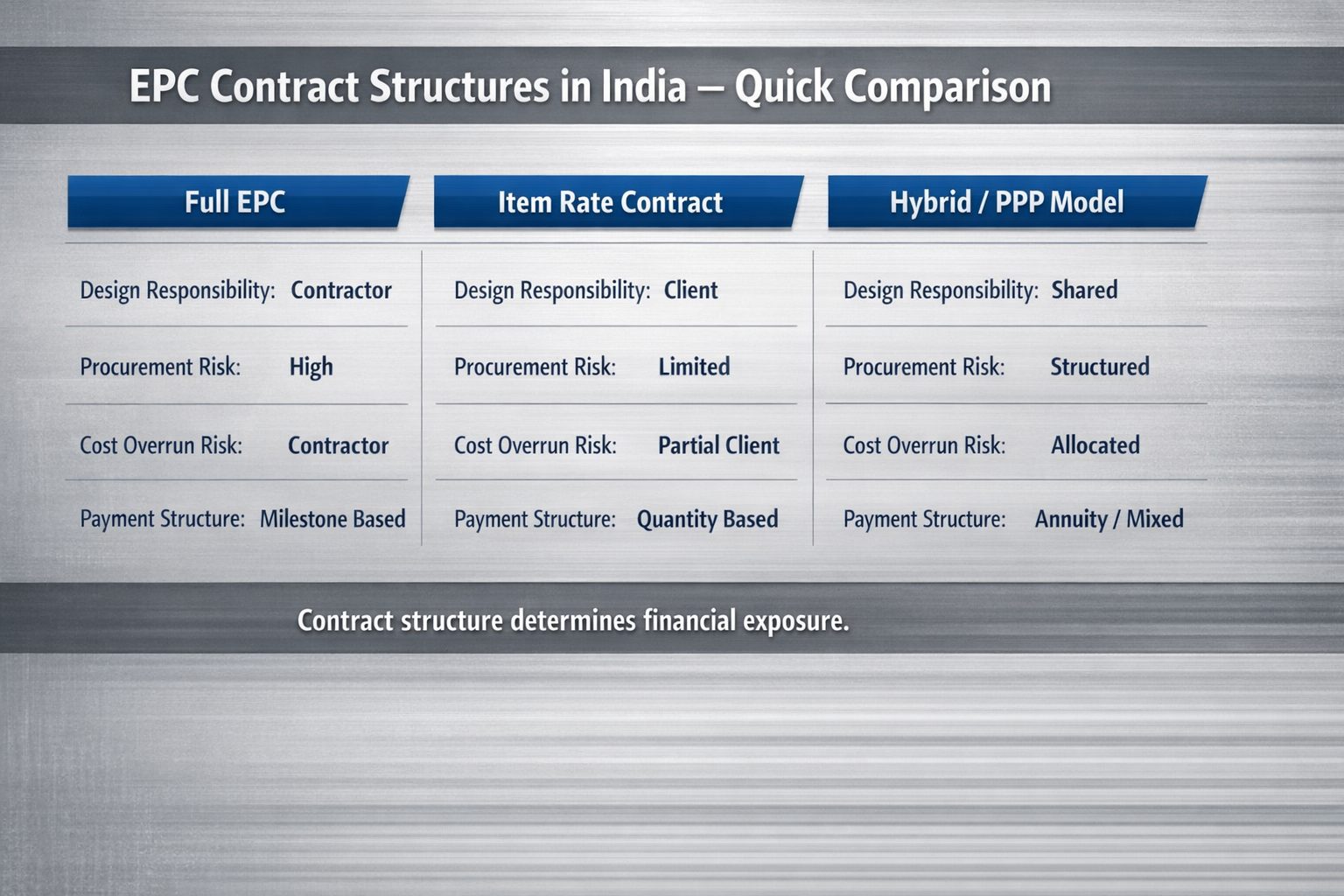
Full EPC vs Item Rate vs Hybrid Contracts
Not all EPC Projects in India follow one uniform structure. Contract type determines liability, capital exposure, and operational pressure. Many MSMEs overlook this before entering Engineering Procurement Construction India bids.
| Parameter | Full EPC | Item Rate Contract | Hybrid / PPP Model |
| Design Responsibility | Contractor | Client | Shared or structured |
| Procurement Risk | Contractor | Limited | Varies |
| Cost Overrun Risk | Contractor | Client partly | Structured allocation |
| Payment Structure | Milestone based | Quantity based | Annuity or mixed |
| MSME Entry Feasibility | Moderate to difficult | Easier | Selective |
In full EPC projects India, accountability sits with one entity. Delays, design errors, or cost escalation remain internal to the contractor.
Item rate contracts reduce engineering liability but require strict quantity compliance. Hybrid structures combine financing and performance obligations, often seen in highway EPC contracts India and renewable energy EPC projects.
EPC project lifecycle
Every EPC project lifecycle in India moves through:
- Detailed engineering and drawings
- Procurement of equipment and raw materials
- Site mobilisation and execution
- Testing and commissioning
- Defect liability and handover
Procurement stages often create more compliance pressure than site execution. Documentation lapses during vendor onboarding frequently delay government EPC tenders India.
EPC contract risk allocation explained
EPC contract risk allocation concentrates responsibility on the contractor. This includes design accuracy, timeline compliance, and performance output. Liquidated damages apply if milestones slip.
For MSME participation in EPC projects, risk awareness matters as much as pricing strategy. Performance bank guarantee EPC clauses and mobilisation advance EPC contract recovery terms must be reviewed carefully before submission.
Sector-wise EPC opportunities in India
Different sectors within EPC Projects in India operate under distinct capital cycles, compliance intensity, execution risk, etc. And choosing the right segment often determines whether an MSME survives its first large contract.
Renewable energy EPC projects
These projects, especially solar and transmission packages, are expanding across states. These contracts involve strict technical specifications and time bound commissioning.
Payment often links to performance validation. Smaller firms usually enter through subcontracting in EPC projects for module mounting, cabling, or civil packages. Documentation review remains critical.
Highway EPC contracts India
Highway EPC contracts India require heavy equipment deployment and strong site management capability. Mobilisation expenses are high.
Hybrid payment models are common. Infrastructure tender eligibility criteria India for road projects usually include turnover and past execution thresholds. Consortium bidding EPC India is often used to meet these conditions.
Metro rail EPC projects
Metro rail EPC projects operate under tight safety and quality norms. Utility coordination and inspection approvals influence billing timelines.
Direct bidding remains difficult for smaller firms. However, package based subcontracting under established EPC contractors in India creates workable entry routes.
Water treatment EPC India
Water treatment EPC India projects focus on municipal plants and industrial treatment systems. Engineering accuracy is closely monitored.
Output performance testing affects final payments. Firms supplying fabricated structures or electrical systems must align with EPC project lifecycle in India milestones.
Power plant EPC contractors
Power plant EPC contractors handle technically complex assignments. Equipment procurement cycles are long.
For MSME participation in EPC projects within this segment, financial planning is essential due to extended inspection and approval stages.
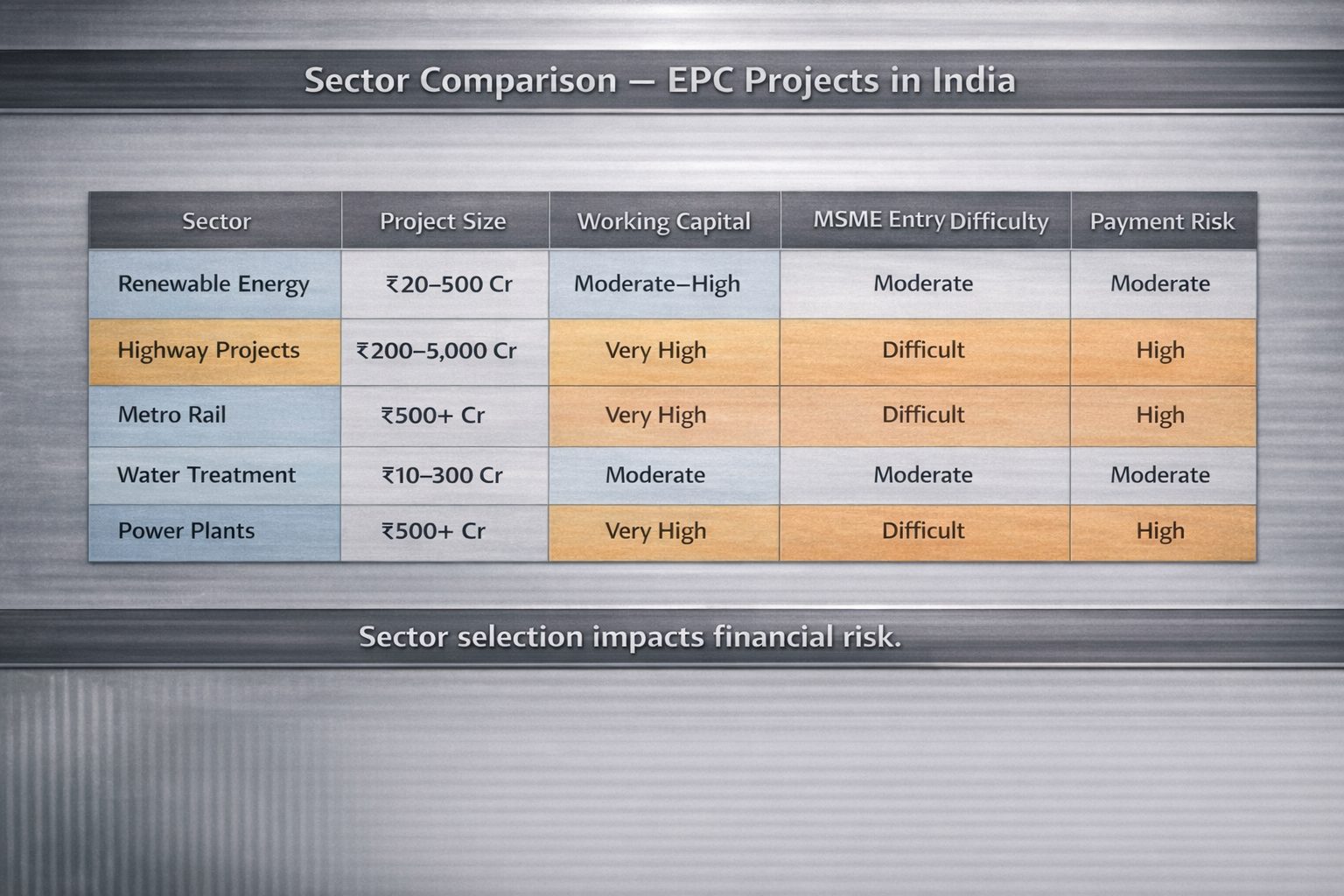
Sector comparison snapshot
The scale and exposure vary sharply across segments within EPC Projects in India. A structured comparison helps in realistic assessment.
| Sector | Typical Project Size | Working Capital Intensity | Documentation Complexity | MSME Entry Difficulty | Payment Cycle Risk |
| Renewable Energy EPC Projects | ₹20–500 Cr. | Moderate to High | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Highway EPC Contracts India | ₹200–5,000 Cr. | Very High | High | Difficult as Prime | High |
| Metro Rail EPC Projects | ₹500–10,000 Cr. | Very High | Very High | Difficult as Prime | High |
| Water Treatment EPC India | ₹10–300 Cr. | Moderate | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Power Plant EPC Contractors | ₹500 Cr. and above | Very High | Very High | Difficult | High |
The EPC bidding process in India
Winning EPC Projects in India depends less on pricing and more on compliance accuracy. Many technically capable firms fail during documentation screening. Let’s see why.
Where government EPC tenders in India are published
Most government EPC tenders in India appear on central and state e-procurement portals. Public sector EPC projects in India publish detailed eligibility and scope documents along with timelines.
Private EPC companies in India usually follow structured vendor registration before issuing tenders. MSMEs must monitor both systems consistently to avoid missing bid windows.
Infrastructure tender eligibility criteria in India
Infrastructure tender eligibility criteria in India typically include:
- Minimum turnover requirements
- Net worth certification
- Similar project experience
- Technical manpower details
- Machinery ownership or lease proof
These conditions determine qualification before price evaluation. MSME participation in EPC projects improves when eligibility gaps are identified early.
EPC tender documents in India – Clauses that need attention
EPC tender documents in India contain commercial terms, scope definitions, and EPC compliance requirements in India.
Particular care is required when reviewing:
- EPC contract risk allocation
- Performance bank guarantee EPC percentage
- Mobilisation advance EPC contract recovery terms
- Liquidated damages provisions
Many firms concentrate only on rate calculation. Risk often hides inside contractual clauses.
Why bids get rejected
Common rejection reasons in the EPC bidding process in India include incomplete forms, expired registrations, or incorrect EMD submission.
In real procurement cycles, documentation discipline decides outcomes. In EPC projects in India, compliance precision often matters more than price competitiveness.
Financial exposure and risk planning
Financial risk in EPC Projects in India starts well before the first payment is received. Site setup, material orders, and manpower deployment require upfront spending. Payment release usually follows verification and milestone approval. The gap between spending and recovery needs careful planning.
Performance bank guarantee EPC
After award, most contracts require a performance bank guarantee EPC. The bank blocks a fixed percentage of the contract value. This limit stays locked until project completion or defect liability closure.
For MSMEs, this reduces available working capital. Bidding without checking banking limits can restrict day to day operations.
Mobilisation advance EPC contract
Some EPC projects in India provide mobilisation advance to support initial expenses. The amount is later deducted from running bills.
If billing slows due to inspection delays or measurement disputes, deductions continue while fresh inflow slows. This situation is common in large infrastructure projects in India.
Working capital planning
Material suppliers expect timely payment. Labour costs are weekly or monthly. Equipment hire is fixed. However, bill certification under government EPC tenders in India may take time.
MSME participation in EPC projects becomes safer when internal cash flow is mapped against project milestones.
EPC project financing India
Banks assess turnover history and past execution record before extending credit. Conservative projections reduce pressure during execution.
In EPC projects in India, stable cash management often matters more than quoted profit margins.
Strategic entry models for MSMEs
Not every firm can bid directly for large EPC Projects in India. Entry often happens in stages. A planned approach reduces risk and builds experience over time.
Consortium bidding EPC India
Consortium bidding EPC India allows two or more firms to combine technical and financial strength. This model helps meet infrastructure tender eligibility criteria in India where turnover or experience requirements are high.
Clear role division is essential. Responsibility for design, execution, and financial guarantees must be defined before submission. Disputes within the consortium can affect project delivery.
Subcontracting in EPC projects
Subcontracting in EPC projects remains the most common route for MSME participation in EPC projects. Large EPC contractors in India divide work into packages such as civil works, fabrication, cabling, or equipment supply.
This route reduces direct contractual exposure. However, payment timelines depend on the main contractor’s billing cycle. Terms should be reviewed carefully before acceptance.
Partnering with private EPC companies in India
Private EPC companies in India often maintain approved vendor lists. Registration improves visibility for repeat work.
Consistent quality and timely delivery build long term relationships. Smaller package execution helps strengthen credentials for future bidding.
Vendor registration in public sector EPC projects in India
Public sector EPC projects in India require formal registration and compliance documentation. Eligibility proof must be updated regularly.
A gradual entry strategy supports sustainable growth in EPC projects in India.
Conclusion
In 2026, EPC Projects in India continue to expand across infrastructure, energy, transport, and utilities. The opportunity is significant, but execution demands discipline. Preparation, capital planning, and documentation accuracy remain essential.
Preparation over aggressive bidding
In government EPC tenders in India, compliance gaps still eliminate bids before pricing is reviewed. Careful study of EPC tender documents in India, infrastructure tender eligibility criteria in India, and EPC contract risk allocation protects firms from avoidable rejection.
Pricing strategy alone is rarely enough.
EPC participation as a long-term strategy
MSME participation in EPC projects in 2026 requires phased growth. Subcontracting in EPC projects and consortium bidding EPC India provide structured entry routes.
In EPC projects in India, consistent execution and strong cash management create durable progress. Expansion without planning increases exposure.
Looking to procure steel?
Tata nexarc helps manufacturers, builders and MSMEs source certified steel products, compare prices, and choose the right grade as per IS codes—with complete traceability and procurement confidence.
FAQs
What is the typical contract duration for EPC Projects in India?
Do EPC contracts allow price escalation for raw materials?
How important is project scheduling software in EPC execution?
Can MSMEs bid for international EPC projects from India?
What insurance policies are mandatory in EPC contracts?
Are joint ventures different from consortium bidding in EPC?
How are variation orders handled in EPC contracts?
What role do project management consultants play in EPC projects?
Can digital documentation improve EPC bid success rates?
How critical is vendor evaluation in EPC procurement?
Charul is a content marketing professional and seasoned content writer who loves writing on various topics with 3 years of experience. At Tata nexarc, it has been 2 years since she is helping business to understand jargon better and deeper to make strategical decisions. While not writing, she loves listing pop music.