Table of Contents
Introduction
In 2026, many firms still confuse billing with cash received. The EPC payment cycle in India works differently. Work may progress on site, yet funds may not arrive on time. The delay sits between execution, certification, and payment release.
How the EPC billing structure creates gaps
The EPC billing cycle India runs on milestone billing and running account submissions. Each bill passes through measurement checks and layered approvals. Even small documentation gaps can trigger running account (RA) bill approval delay.
Meanwhile, retention money in EPC projects and performance bank guarantee lock-in reduce available liquidity. The result is an EPC working capital gap, even on profitable contracts.
This guide explains how the EPC payment cycle in India functions, where cash flow gets stuck, how subcontractor payment delay EPC occurs, and what practical steps businesses can take to stabilise cash flow in infrastructure projects.
Understanding the EPC payment cycle in India
Before fixing delays, businesses must understand how the EPC payment cycle in India is structured.
Milestone-based billing structure
Most EPC contracts follow milestone billing. Payment links to certified progress, not daily work. If one milestone slips, the EPC billing cycle India shifts immediately.
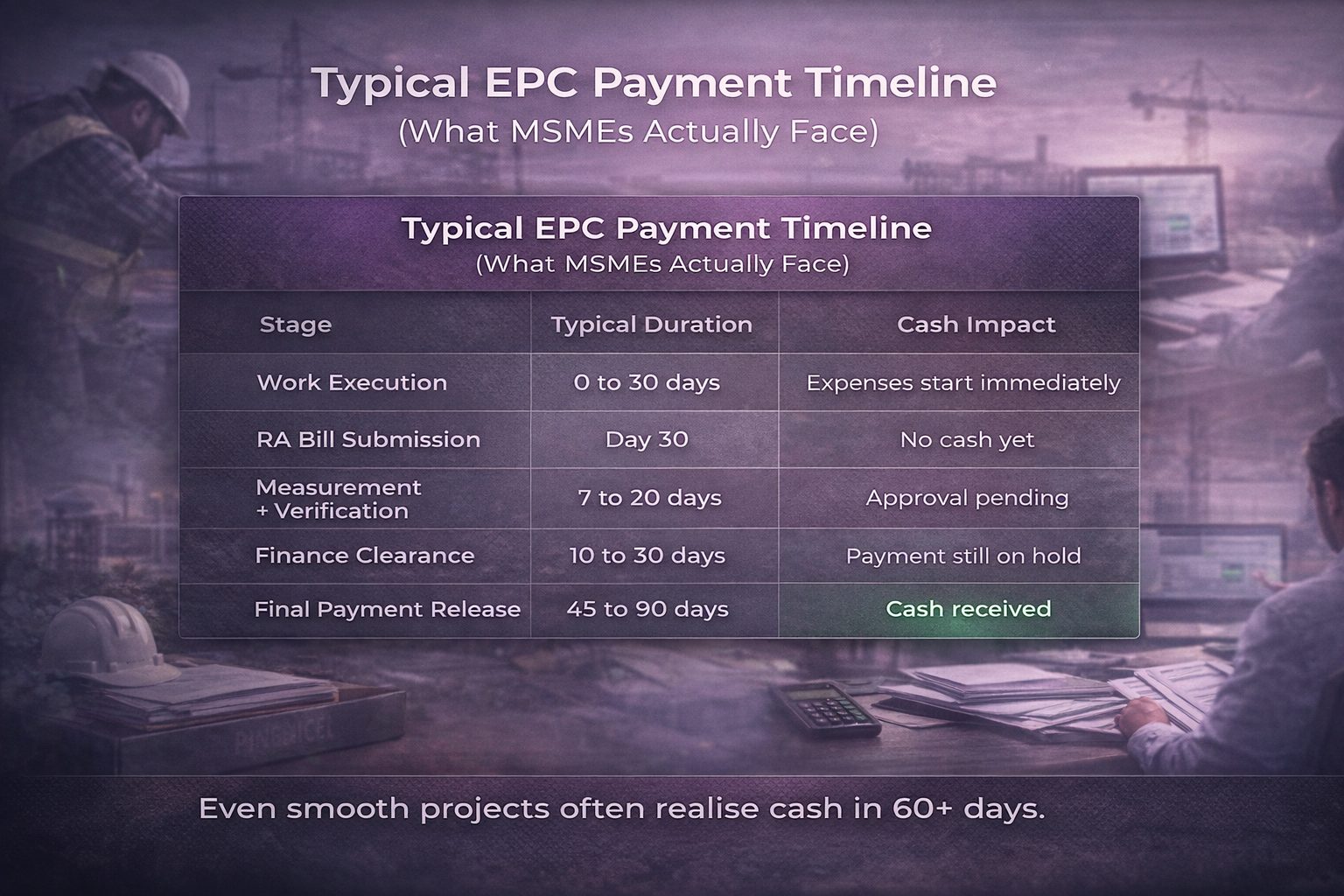
Typical payment timeline in infrastructure projects
The table below shows how time expands inside the EPC payment cycle in India:
| Stage | Typical Duration | Cash Impact |
| Work execution | 0–30 days | Expenses begin immediately |
| RA Bill submission | Day 30 | No cash yet |
| Measurement & verification | 7–20 days | Approval pending |
| Finance clearance | 10–30 days | Payment still on hold |
| Final payment release | 45–90 days | Cash received |
Even in smooth projects, realisation may take 60 days or more. During this period, labour, material, and logistics payments continue.
Retention and deductions
Retention money in EPC projects usually ranges from 5 to 10 percent of each bill. This amount remains blocked until project completion or defect liability period retention closure.
Mobilisation advance recovery terms also reduce early-stage inflow. Combined, these deductions create an EPC working capital gap even when billing appears steady.
Understanding these numbers makes cash flow management in infrastructure projects more realistic.
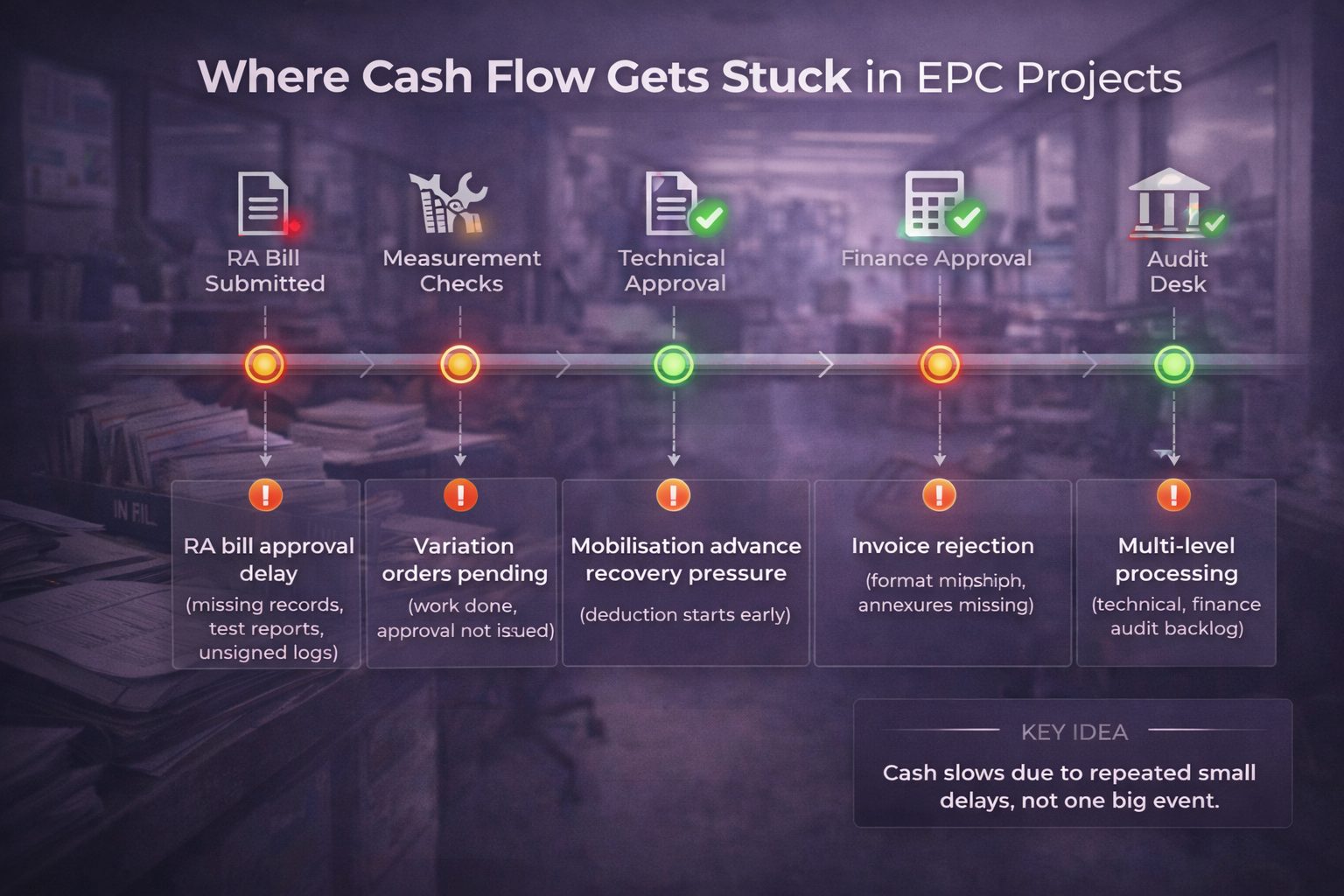
Where cash flow gets stuck in EPC projects
Even when the EPC payment cycle in India looks clear on paper, cash slows down at specific points. These bottlenecks repeat across sectors.
RA bill approval delay
The most common issue is RA bill approval delay. After submission, measurements may require revalidation. Quantity differences, missing test reports, or unsigned site records pause running account bill certification.
A delay of even 15 days per cycle compounds over six months. This pattern widens the EPC project cash flow India gap.
Variation orders without formal approval
Scope changes occur frequently in infrastructure projects. However, work sometimes proceeds before written approval.
If variation orders lack formal sanction, billing for additional work stalls. Funds remain unapproved despite physical completion.
Mobilisation advance recovery pressure
Mobilisation advance recovery terms begin from early bills. If billing slows but recovery continues, net inflow reduces sharply.
For MSMEs, this mismatch strains working capital faster than expected.
Invoice rejection and documentation gaps
EPC invoice rejection reasons often include format errors, missing annexures, or mismatch with EPC contract payment terms India.
In real procurement cycles, small documentation gaps create large financial pauses.
Multi-level government processing
In the government EPC payment process India, files move across technical, finance, and audit desks.
During peak workload periods, infrastructure project payment delays India extend beyond planned timelines.
Cash rarely stops due to one issue. It slows due to repeated small delays within the EPC payment cycle in India.
Quick diagnostic snapshot
| Delay Source | Typical Impact on Payment | Business Effect |
| RA Bill Approval Delay | 15–30 days | Working capital strain |
| Variation Order Pending | 30–90 days | Unbilled completed work |
| Advance Recovery | Immediate deduction | Reduced net inflow |
| Invoice Rejection | 7–20 days | Reprocessing delay |
| Multi-Level Approvals | 20–60 days | Payment cycle extension |
When multiple delays combine, the EPC payment cycle in India stretches far beyond planned timelines.
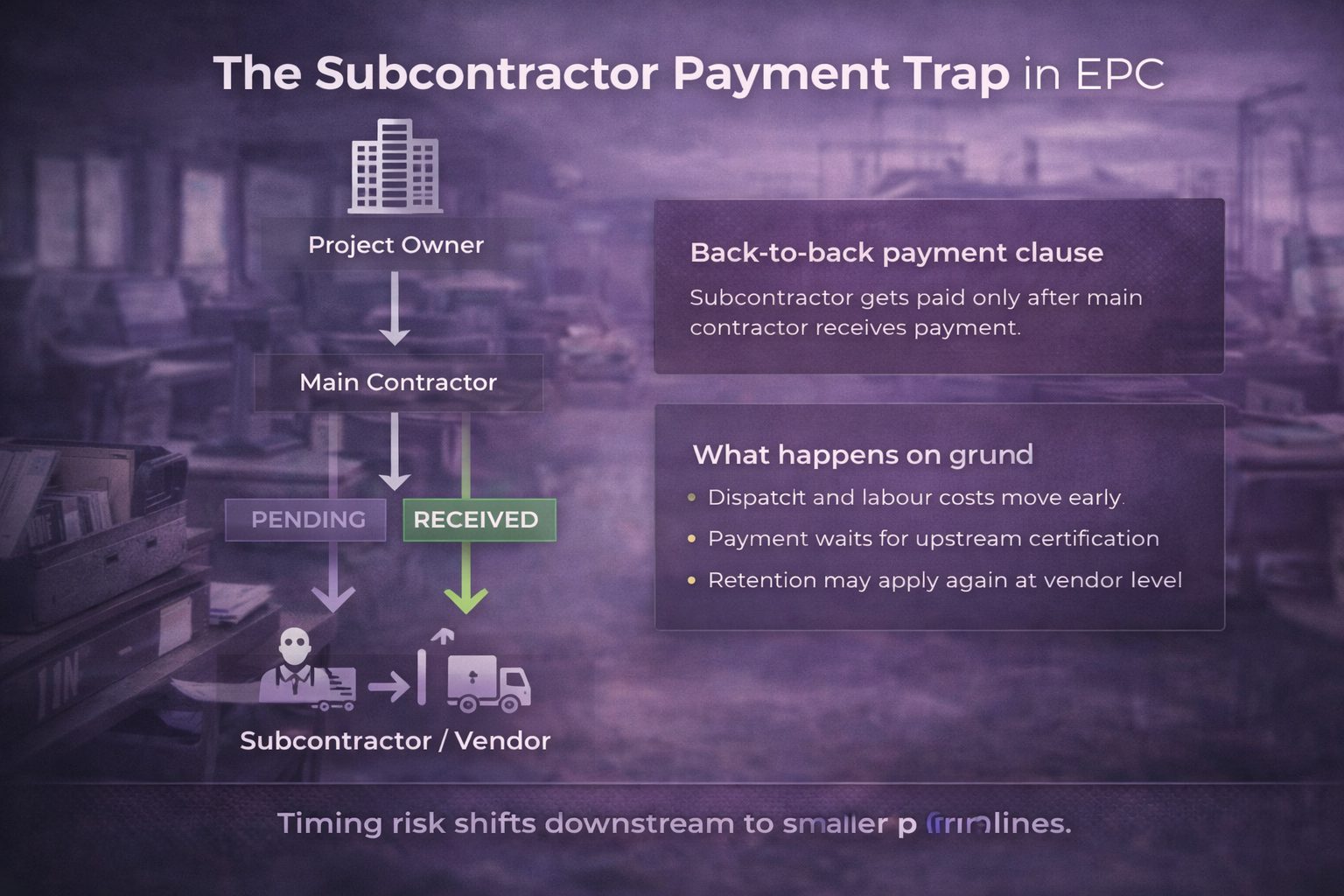
The subcontractor payment trap
The EPC payment cycle in India affects subcontractors more sharply than main contractors. Payment does not move directly from project owner to every executing vendor. It flows in layers.
Payment flow structure
In most projects, the client releases funds to the main contractor after running account bill certification. The main contractor then clears dues to subcontractors.
If the upstream payment slows, subcontractor payment delay EPC becomes immediate. Site execution may continue, but cash does not.
Back-to-back payment clauses
Many subcontract agreements include a back-to-back payment clause EPC. This means the subcontractor receives payment only after the main contractor receives funds from the client.
On paper, the clause looks standard. In practice, it transfers timing risk downstream. The EPC working capital gap shifts to smaller firms.
Impact on MSME vendors
Consider a fabrication vendor supplying structural components under a metro package. Dispatch happens in week two. Transport cost and labour payments move immediately.
However, payment depends on the main contractor’s billing cycle. If infrastructure project payment delays India extend beyond 60 days, the vendor absorbs the shock.
Retention money in EPC projects may also apply at subcontract level, further tightening liquidity.
Within the EPC payment cycle in India, subcontractors must evaluate contract clauses as carefully as pricing.
Financial pressure points in the EPC payment cycle
Even when the EPC payment cycle in India runs as planned, certain financial locks reduce liquidity. These pressure points are built into most EPC contract payment terms India.
Performance bank guarantee lock-in
After award, contractors submit a performance bank guarantee. Banks block a percentage of the contract value against existing limits.
This performance bank guarantee lock-in reduces available credit for day-to-day operations. For MSMEs, this directly affects EPC project cash flow India.
Retention money accumulation
Retention money in EPC projects typically ranges from 5 to 10 percent of each certified bill. Over multiple billing cycles, this amount accumulates.
If a project runs for 18 to 24 months, a significant portion of revenue remains locked until defect liability period retention ends.
Working capital vs billing gap
Expenses such as labour, diesel, transport, and raw material move weekly. Certification and fund release follow monthly or longer cycles.
This mismatch creates an EPC working capital gap. Even profitable contracts can feel strained during peak execution stages.
Price escalation and payment terms
Some contracts limit escalation benefits or delay approval of revised rates. If raw material prices rise, recovery may lag behind cost increase.
Without careful EPC project finance planning, this gap widens.
In the EPC payment cycle in India, pressure rarely comes from one deduction. It builds through cumulative financial locks.
Practical fixes to stabilise cash flow
The EPC payment cycle in India cannot be changed easily. However, its impact can be managed. Businesses that plan billing and documentation early face fewer shocks.
Build a structured billing calendar
Link internal project tracking to the EPC milestone billing structure. Record execution progress daily. Prepare supporting documents before RA bill submission.
Early preparation reduces RA bill approval delay. In real procurement cycles, organised paperwork speeds up running account bill certification.
Strengthen documentation before submission
Create a pre-submission review system. Verify quantity sheets, test reports, dispatch records, and tax details before uploading invoices.
Many EPC invoice rejection reasons arise from small mismatches. Preventing rejection shortens the EPC billing cycle India.
Negotiate payment clauses at contract stage
Before signing, review EPC contract payment terms India carefully. Clarify retention percentage, certification timelines, and mobilisation advance recovery terms.
Clear timelines reduce future disputes. Small clause corrections protect EPC project cash flow India later.
Use financial tools strategically
Bill discounting and structured credit facilities support EPC receivables management. This route is gaining attention among MSME contractors handling multiple projects.
Conservative EPC project finance planning reduces stress during infrastructure project payment delays India.
Managing the EPC payment cycle in India requires discipline at both project and finance levels.
How MSMEs should evaluate EPC projects before bidding
The EPC payment cycle in India should be assessed before a bid is submitted. Many firms study scope and margin but ignore cash timing. That oversight creates pressure later.
Simulate cash flow before quoting
Estimate execution cost month by month. Compare it with expected billing under the EPC milestone billing structure.
If certification takes 60 days and expenses move every 15 days, an EPC working capital gap will appear. Simulation reveals whether internal reserves can handle that gap.
Review the client’s payment record
Not all infrastructure project payment delays India follow the same pattern. Some authorities clear bills within 30 days. Others move slower.
Review past contractor feedback and project timelines. The government EPC payment process India varies across departments.
Examine contract-level risk clauses
Study EPC contract payment terms India carefully. Check retention money in EPC projects percentage, defect liability period retention duration, and mobilisation advance recovery terms.
Back-to-back payment clause EPC in subcontract agreements should also be evaluated before commitment.
In the EPC payment cycle in India, prevention begins at the bidding stage. Careful evaluation reduces stress during execution.
Conclusion
The EPC payment cycle in India rarely fails because a project lacks margin. It slows because cash release follows layered certification, retention deductions, and structured recovery terms. Profit on paper does not guarantee liquidity in the bank.
For MSMEs, understanding the EPC billing cycle India before bidding makes a measurable difference. RA bill approval delay, retention money in EPC projects, and performance bank guarantee lock-in must be factored into cash planning from day one.
Strong EPC receivables management, disciplined documentation, and realistic EPC project finance planning reduce exposure during infrastructure project payment delays India.
The EPC payment cycle in India cannot be redesigned by individual contractors. It can, however, be managed with clarity, preparation, and financial control.
Looking to procure steel?
Tata nexarc helps manufacturers, builders and MSMEs source certified steel products, compare prices, and choose the right grade as per IS codes—with complete traceability and procurement confidence.
FAQs
Can payment terms vary between central and state EPC contracts in India?
Is GST timing linked to the EPC payment cycle in India?
Can arbitration delay final payment in EPC projects?
Do lenders consider the EPC payment cycle before sanctioning project finance?
Can digital project management tools reduce billing delays?
Does partial milestone completion allow proportionate billing?
Are tax deductions at source a factor in EPC cash flow planning?
Can delayed site handover impact the EPC billing cycle in India?
Do consortium partners share payment risk equally?
Is retention money ever replaced with bank guarantees?
Charul is a content marketing professional and seasoned content writer who loves writing on various topics with 3 years of experience. At Tata nexarc, it has been 2 years since she is helping business to understand jargon better and deeper to make strategical decisions. While not writing, she loves listing pop music.